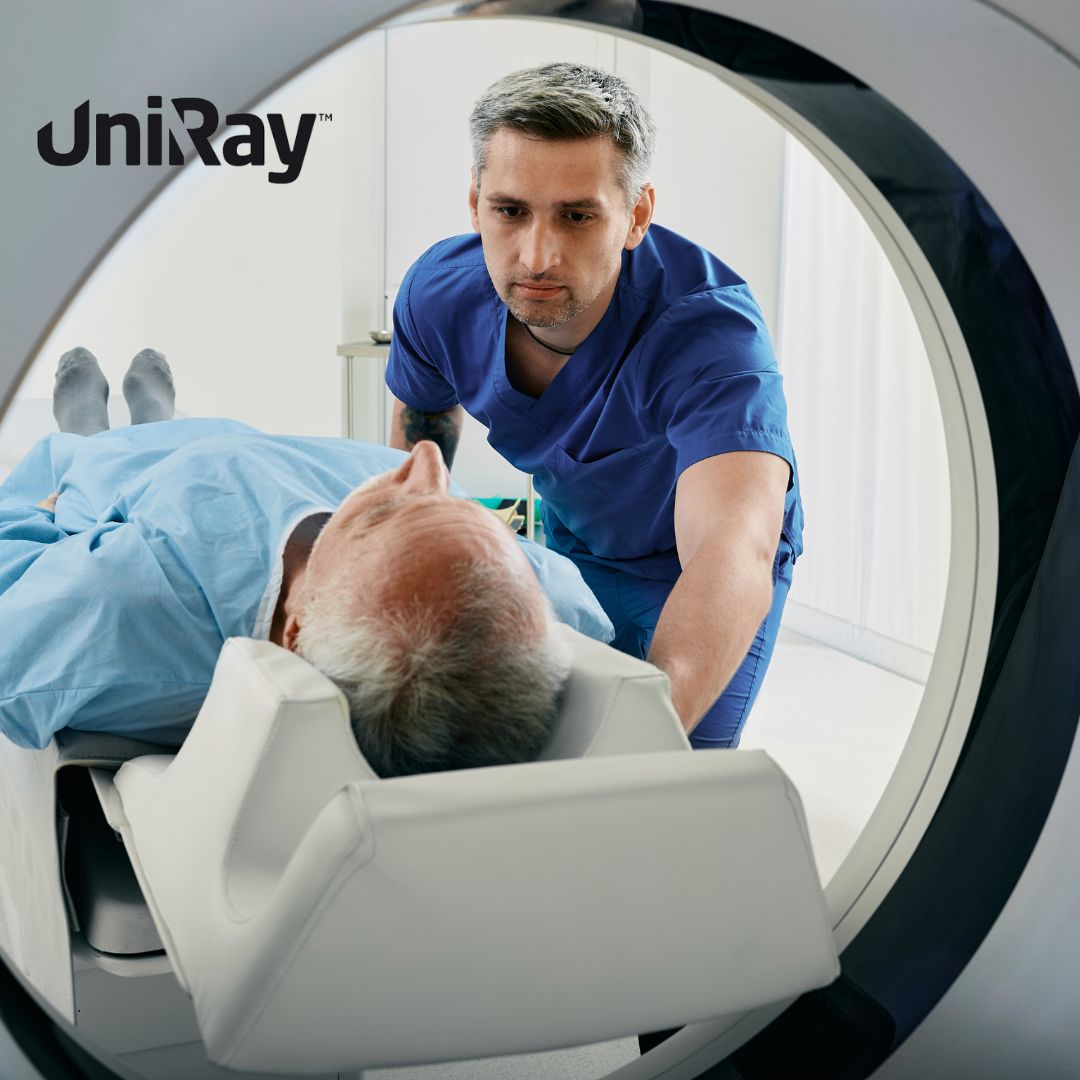
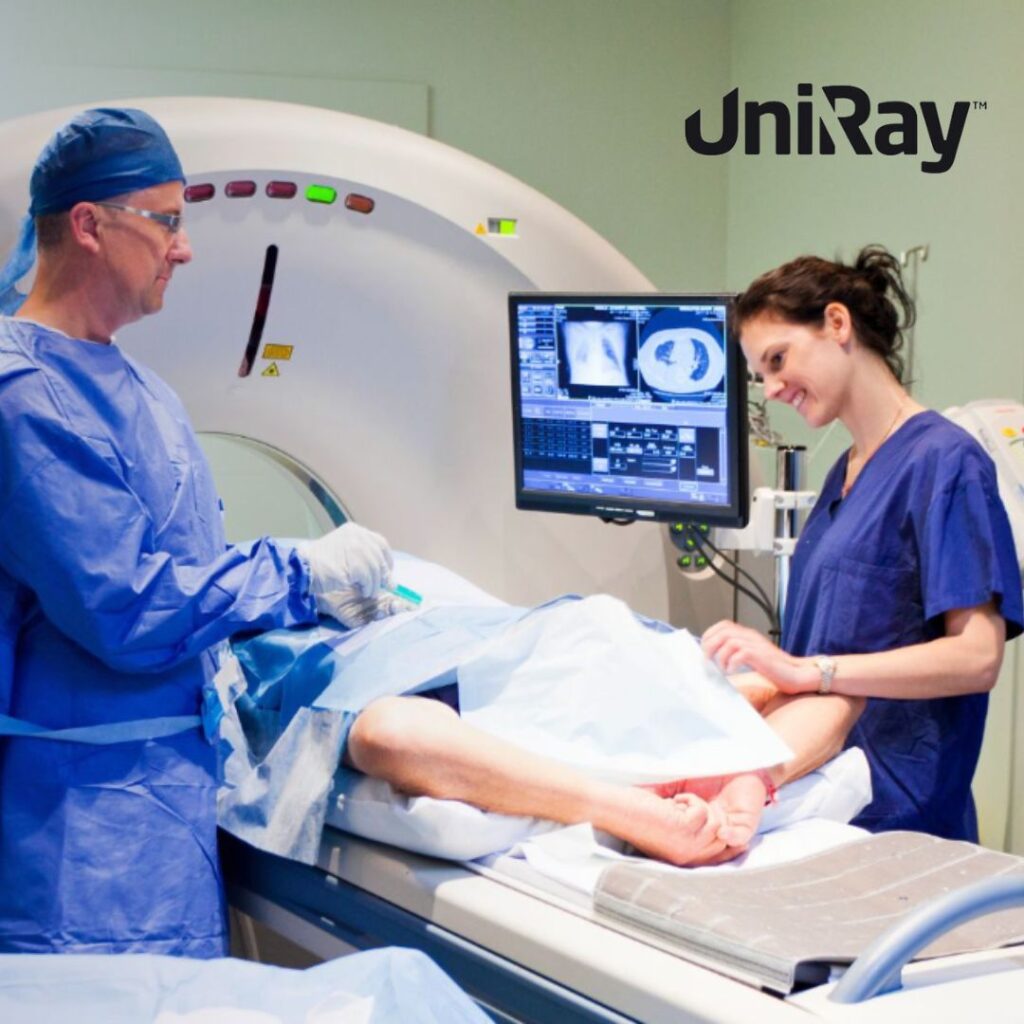
Radiation safety in hospitals is a critical concern in the healthcare industry, especially as medical imaging technologies become increasingly sophisticated and widespread. With the ability to provide invaluable insights into patient conditions, imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and fluoroscopy have become essential tools in modern medicine. However, the use of ionizing radiation also poses risks, making effective radiation protection measures vital for both patient and staff safety. This blog will delve into the principles and practices of medical radiation safety, focusing on radiation safety in hospitals, radiology protection, and broader medical radiation safety measures.
Understanding Radiation Safety in Hospitals
Radiation safety encompasses the policies, procedures, and equipment necessary to minimize exposure to ionizing radiation in a healthcare setting. Hospitals must adopt stringent radiation safety protocols to ensure that patients, staff, and visitors are protected from unnecessary radiation exposure. This involves not only implementing technical safeguards and safety protocols but also promoting a culture of safety among healthcare professionals.
In the hospital environment, radiation safety involves the following key aspects:
- Knowledge and Training: Healthcare staff must be well-trained in radiation safety protocols to understand the potential risks associated with ionizing radiation and how to mitigate them. Continuous education and training ensure that staff members are updated on the latest safety practices and technological advancements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Hospitals must comply with local, national, and international regulations governing radiation safety. This includes adherence to guidelines set forth by organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP).
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular maintenance and calibration of radiological equipment are essential to ensure optimal performance and minimize unnecessary radiation exposure. Hospitals must implement routine quality control measures to verify that all imaging devices operate within safe limits.
- Patient and Staff Monitoring: Effective monitoring of radiation doses received by patients and healthcare staff is crucial. Implementing dose-tracking systems helps to identify trends and manage exposure levels, ensuring that they remain within acceptable limits.
- Patient Safety Protocols: Hospitals should adopt safety protocols that prioritize patient safety during radiological procedures. This includes using the lowest possible radiation dose while achieving diagnostic quality images and employing alternative imaging techniques when feasible.
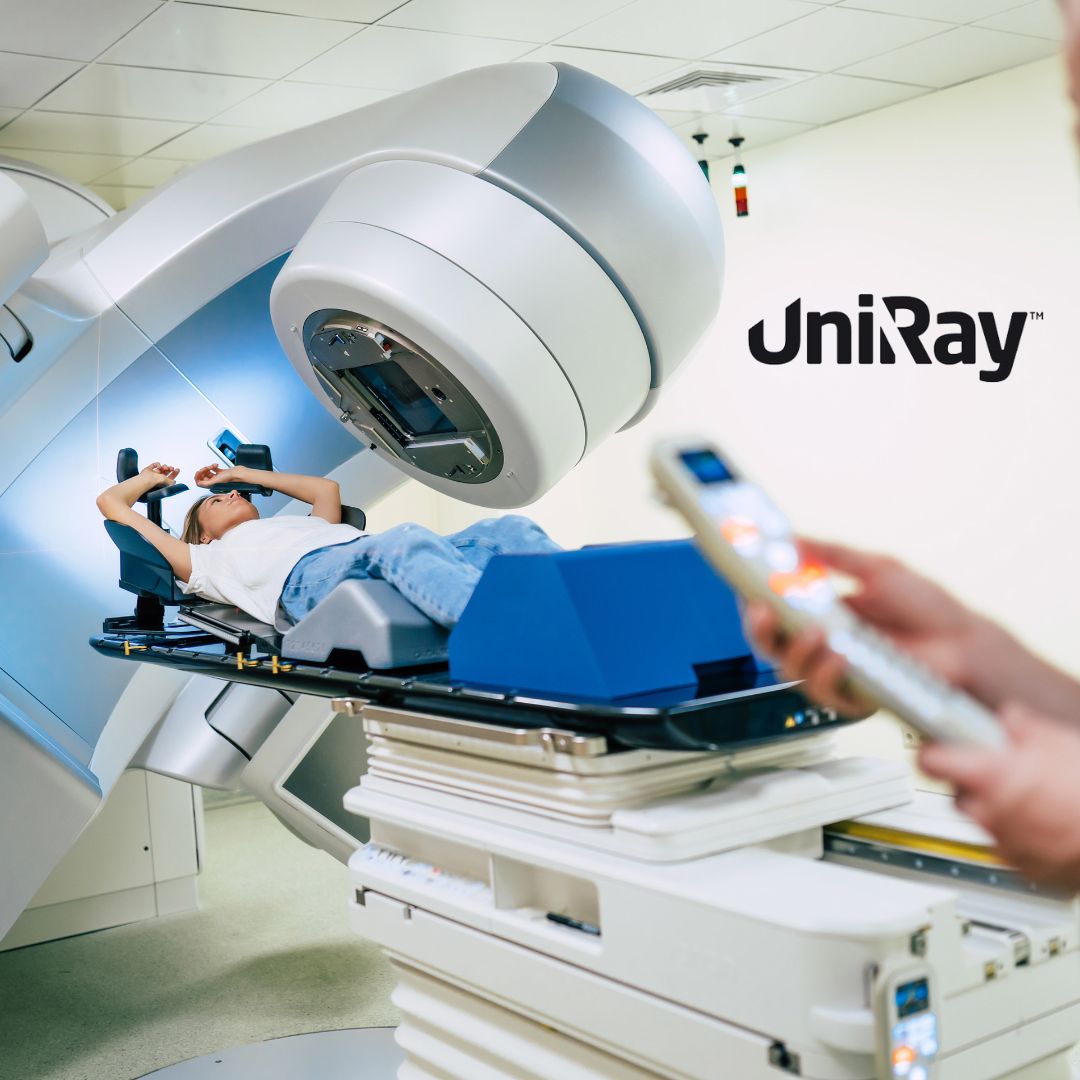 Radiology Protection: Principles and Practices
Radiology Protection: Principles and Practices
Radiology protection is a specialized area of radiation safety that focuses on safeguarding individuals from the harmful effects of radiation during diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The principles of radiology protection can be summarized by the ALARA principle, which stands for “As Low As Reasonably Achievable.” This principle emphasizes minimizing radiation exposure while ensuring that diagnostic quality is maintained. Key strategies for implementing radiology protection in hospitals include:
- Justification: Before conducting any radiological procedure, healthcare providers must assess whether the benefits outweigh the potential risks. Procedures should only be performed when they provide significant diagnostic or therapeutic value to the patient.
- Optimization: Hospitals must optimize imaging techniques to ensure that radiation doses are kept as low as possible while still achieving high-quality images. This involves selecting appropriate imaging protocols, using shielding devices, and applying advanced imaging technologies that require less radiation.
- Limiting Exposure Time: Reducing the duration of exposure to radiation is vital for minimizing dose. Techniques such as employing fast imaging sequences and utilizing digital technology can help achieve this goal.
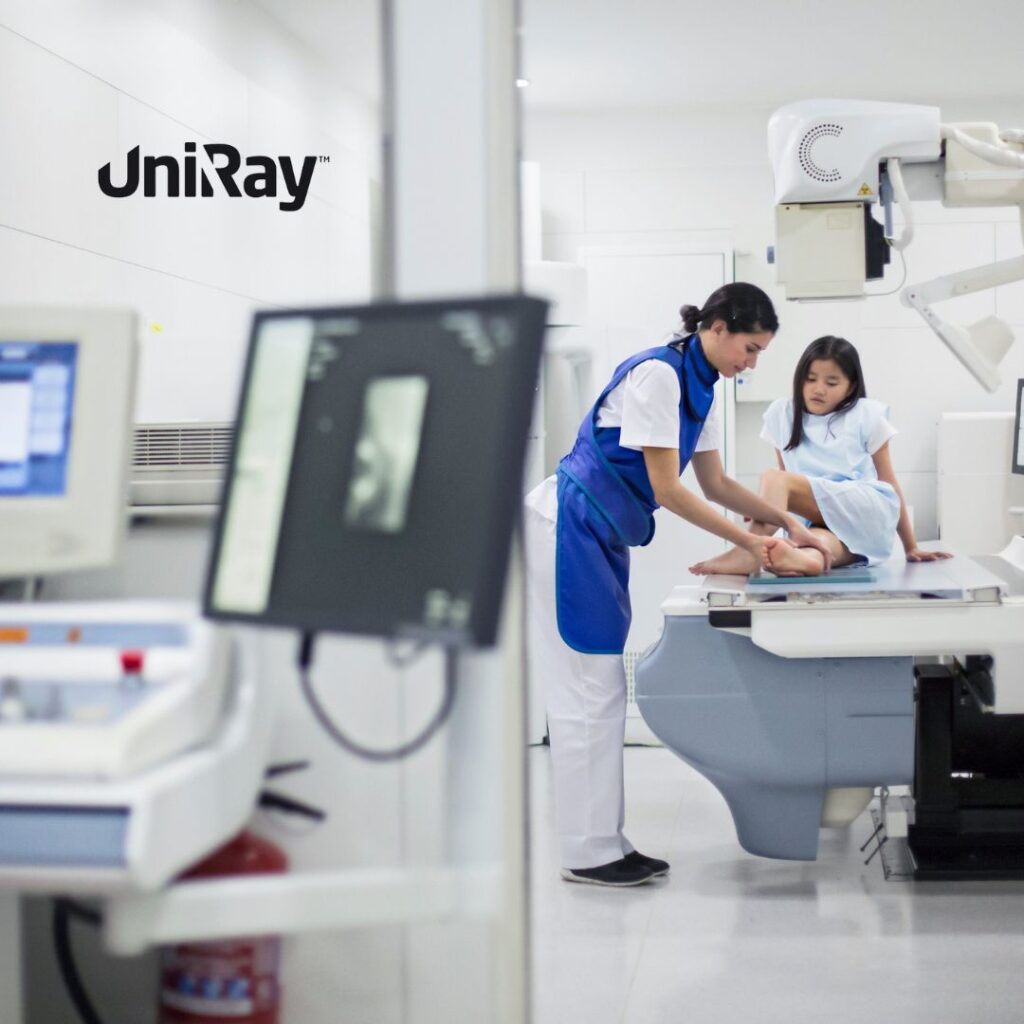
- Distance and Shielding: Maintaining a safe distance from the radiation source is an effective way to reduce exposure. Additionally, utilizing lead aprons, shields, and barriers can protect both patients and staff from scattered radiation.
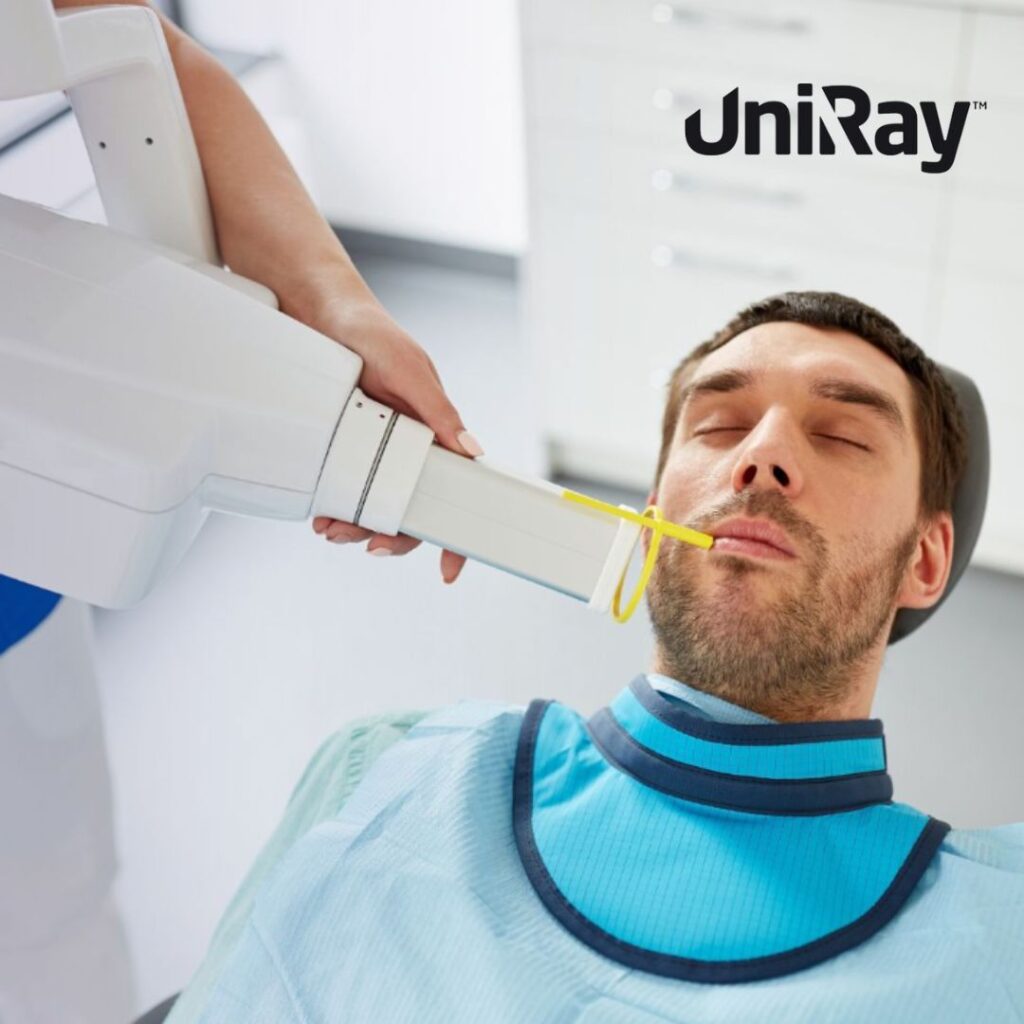
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The use of PPE is essential in radiology protection. Radiology staff should wear lead aprons, thyroid shields, and lead glasses when necessary to minimize exposure during procedures.
Medical Radiation Safety: A Holistic Approach
Medical radiation safety goes beyond just protecting individuals involved in radiological procedures; it encompasses a broader approach to ensuring safety across all healthcare practices that utilize ionizing radiation. Here are some key components of a holistic approach to medical radiation safety:
- Patient Education and Informed Consent: Educating patients about the potential risks and benefits of radiological procedures is essential. Informed consent ensures that patients understand what to expect and can make informed decisions regarding their care.
- Emergency Preparedness: Hospitals should have emergency protocols in place for handling radiation accidents or incidents. Staff must be trained to respond effectively in case of a radiological emergency to minimize risks to patients and the healthcare team.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaboration among different healthcare departments is vital for effective medical radiation safety. Radiologists, technicians, nurses, and administrators should work together to create and implement comprehensive safety protocols.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering data on radiation exposure levels and incidents can help identify areas for improvement. Hospitals should analyze trends and outcomes to continuously refine safety practices and protocols.
- Investing in Technology: Advances in technology can enhance radiation safety in hospitals. For example, using dose-reduction software, advanced imaging techniques, and radiation monitoring devices can help achieve better patient outcomes with lower exposure levels.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Radiation Safety
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring radiation safety in hospitals. Organizations such as the IAEA, NCRP, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set guidelines and standards that healthcare facilities must adhere to. These organizations provide valuable resources and support for hospitals aiming to improve their radiation safety programs.
Hospitals should regularly assess their compliance with regulatory standards and actively engage in quality improvement initiatives. This may involve conducting audits, participating in accreditation programs, and collaborating with regulatory agencies to ensure that best practices are followed.
Conclusion
Radiation safety in hospitals is a multi-faceted challenge that requires a commitment to best practices and a culture of safety. By focusing on radiology protection, implementing comprehensive medical radiation safety measures, and adhering to regulatory guidelines, hospitals can protect patients, staff, and the public from unnecessary radiation exposure. Investing in training, technology, and interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to create a safe healthcare environment where the benefits of medical imaging can be harnessed without compromising safety. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, so too must our approach to radiation safety, ensuring that it remains a priority in the pursuit of quality patient care.