Essential Radiation Protection Measures for Patient Safety
 Radiation plays a crucial role in medical imaging, cancer treatment, and various industrial applications. However, exposure to high doses of radiation can pose serious health risks. Implementing radiation protection measures is essential to ensure patient and healthcare worker safety while maximizing the benefits of radiological procedures. In this blog, we will explore key safety measures for radiation, best practices for radiation safety for patients, and standard radiation safety procedures in medical and industrial settings.
Radiation plays a crucial role in medical imaging, cancer treatment, and various industrial applications. However, exposure to high doses of radiation can pose serious health risks. Implementing radiation protection measures is essential to ensure patient and healthcare worker safety while maximizing the benefits of radiological procedures. In this blog, we will explore key safety measures for radiation, best practices for radiation safety for patients, and standard radiation safety procedures in medical and industrial settings.
Understanding Radiation Exposure Risks
Radiation exposure is classified into two main types: ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation, which includes X-rays and gamma rays, has sufficient energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, potentially causing cellular damage and increasing cancer risks. Proper radiation protection measures are vital to minimize these risks, especially in medical environments where radiation is frequently used for diagnostics and treatment.
Key Radiation Protection Measures
Several protective strategies help reduce radiation exposure for both patients and healthcare professionals:
- Time Management: Limiting the duration of exposure to radiation is one of the most effective ways to reduce the dose absorbed by individuals.
- Distance from Radiation Source: The intensity of radiation decreases with distance. Maintaining a safe distance from radiation-emitting equipment is a fundamental protective measure.
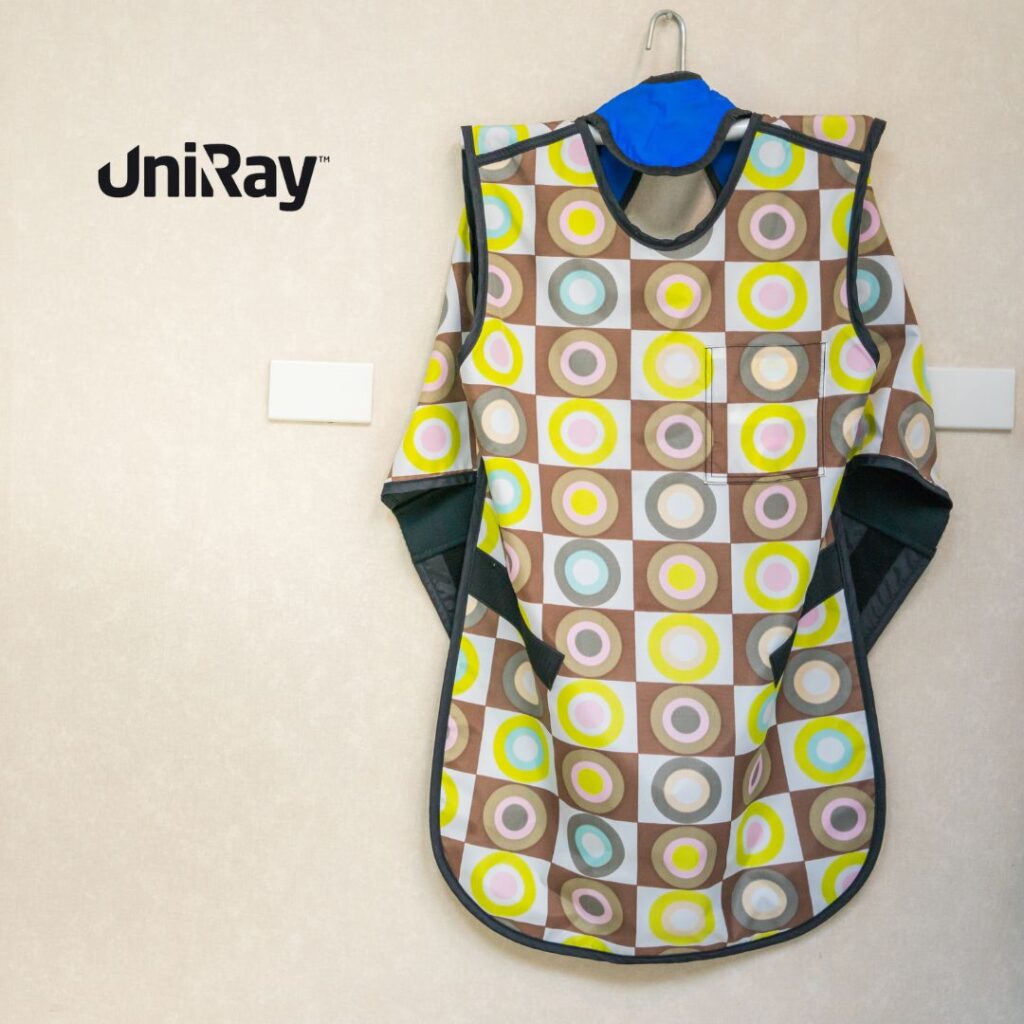
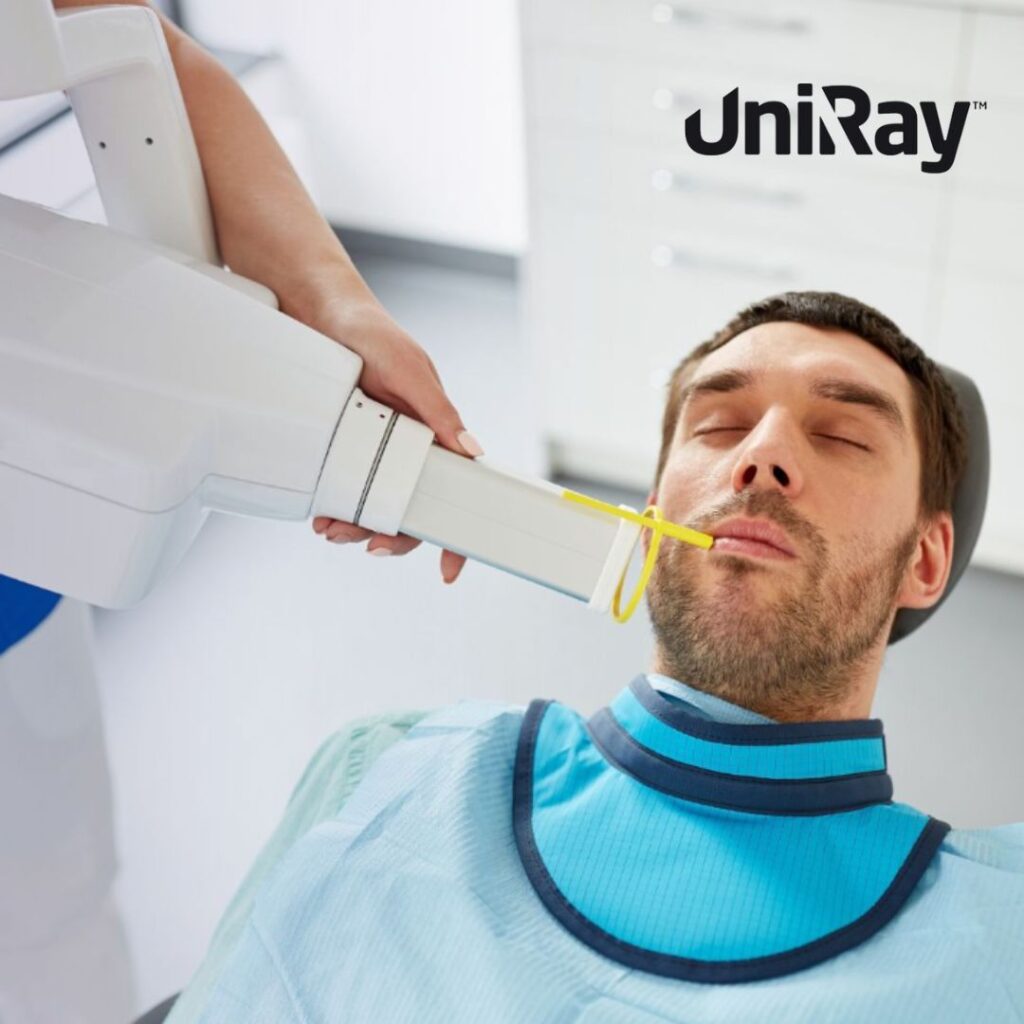
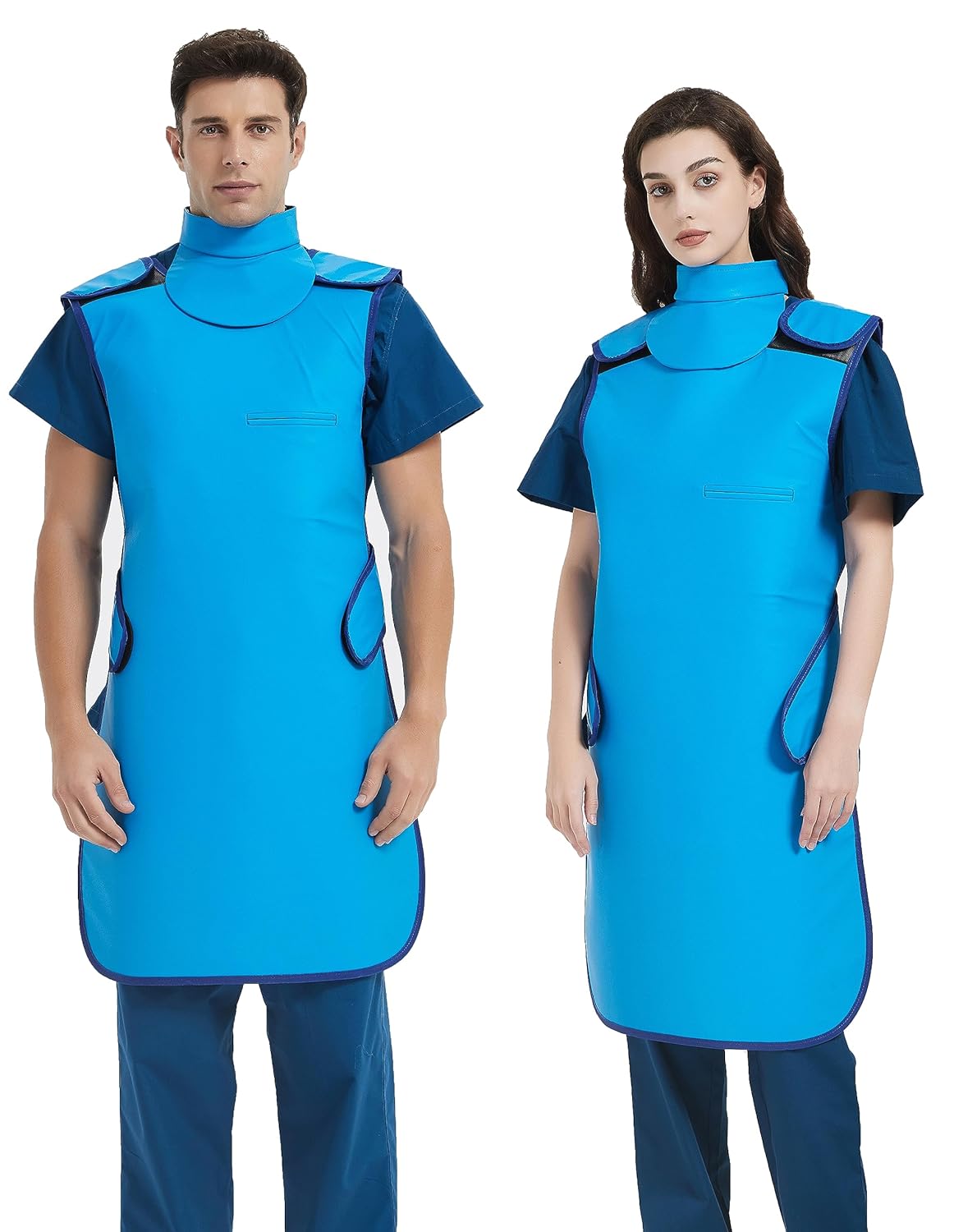
- Shielding: Using protective barriers such as Lead Apron significantly reduces radiation exposure, especially for radiology technicians and patients undergoing X-rays or CT scans.
- Protective Equipment: Apart from lead aprons, other shielding tools like lead gloves, thyroid shields, and leaded glasses provide added protection for sensitive body parts.
- Proper Equipment Handling: Regular maintenance and calibration of radiological equipment ensure accurate radiation output, preventing unnecessary exposure.
Safety Measures for Radiation in Healthcare Settings
Hospitals and diagnostic centers must implement strict safety measures for radiation to protect both patients and medical personnel. Some of the key practices include:
- Radiation Dosimetry Monitoring: Technicians and radiologists should wear dosimeters to monitor accumulated radiation exposure over time.
- Use of Collimators: Collimators help narrow the X-ray beam to the area of interest, minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues.
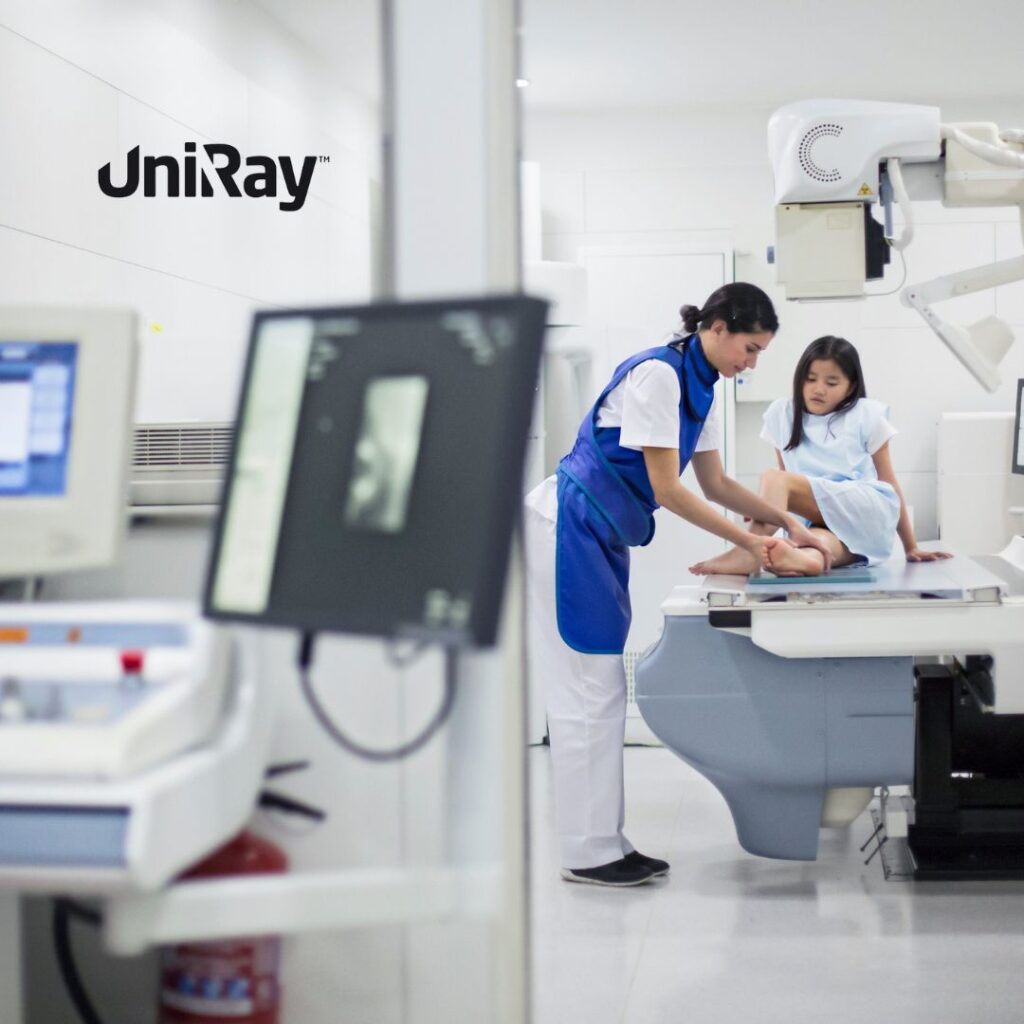
- Patient Positioning Techniques: Proper patient positioning ensures accurate imaging with minimal radiation dose.
- Optimized Imaging Protocols: Modern imaging devices come with dose-reduction technologies that automatically adjust radiation levels based on the required diagnostic outcome.
- Educational Training: Healthcare professionals must undergo regular training in radiation safety to stay updated with the latest protocols and safety regulations.
Radiation Safety for Patients: Minimizing Risks
Ensuring radiation safety for patients is a top priority in medical imaging and radiation therapy. Here are some essential steps taken to protect patients from excessive radiation exposure:
- Use of Radiology Lead Aprons: Patients undergoing X-rays, fluoroscopy, or other radiological exams should wear radiology lead aprons to shield vital organs from unnecessary radiation.
- Pediatric Radiation Safety: Children are more sensitive to radiation than adults, necessitating lower radiation doses and additional protective measures.
- Alternative Imaging Methods: Whenever possible, non-ionizing imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI should be considered as alternatives to X-rays and CT scans.
- Informing Patients: Patients should be informed about the risks and benefits of radiological procedures to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Radiation Safety Procedures: Standard Protocols for Protection
Strict adherence to radiation safety procedures is necessary to minimize the potential hazards associated with radiation exposure. Common protocols include:
- ALARA Principle: The “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” principle ensures that radiation exposure is kept at the minimum necessary level for achieving diagnostic or therapeutic goals.
- Controlled Radiation Zones: Marked areas where radiation levels are higher than normal help restrict unauthorized access and protect individuals from unnecessary exposure.
- Lead-Lined Rooms & Barriers: Radiology departments use lead-lined walls and protective barriers to confine radiation within designated areas.
- Emergency Protocols for Radiation Exposure: Medical facilities must have a clear action plan for dealing with accidental radiation overexposure, including immediate medical assessment and monitoring.
- Routine Safety Audits: Regular inspections and audits of radiation safety practices help ensure compliance with industry regulations and enhance overall safety measures.
Conclusion
Radiation safety is a critical aspect of medical and industrial applications that involve ionizing radiation. Implementing effective radiation protection measures, adopting strict safety measures for radiation, ensuring radiation safety for patients, and following standardized radiation safety procedures can significantly reduce radiation risks. By using protective equipment such as Lead Apron and radiology lead aprons, healthcare professionals can further enhance patient safety and maintain a secure working environment. Prioritizing radiation protection ensures that the benefits of radiological procedures outweigh the risks, promoting better health outcomes for all.