Protecting Yourself: How Lead Aprons Stop Radiation in Medical Imaging

In the field of medical imaging, the use of radiation is crucial for diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions. However, exposure to radiation carries potential risks to both patients and medical professionals. Lead aprons are one of the most commonly used protective measures in medical imaging. These aprons play a vital role in shielding individuals from harmful radiation during X-ray and other imaging procedures. But how do lead aprons stop radiation? In this blog, we will explore the science behind lead aprons, their role in radiation protection, and the importance of using additional protective gear such as thyroid shields.
The Science Behind Lead Aprons and Radiation Protection
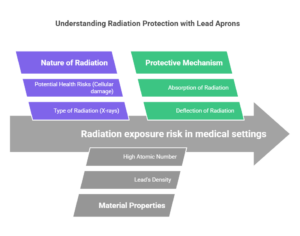
To understand how lead aprons protect against radiation, it’s essential to first understand the nature of radiation and how it interacts with materials. Radiation, in the context of medical imaging, typically comes from X-rays, which are a form of electromagnetic radiation. When X-rays pass through the body, they have the potential to cause cellular damage, which can lead to cancer or other health issues over time.
Lead aprons are made from a combination of lead and other materials, with lead being the primary component that blocks radiation. Lead is dense and has a high atomic number, which makes it an effective shield against X-rays. When X-rays encounter the lead in the apron, the lead absorbs or deflects the radiation, reducing the amount that reaches the body. This process is known as attenuation, where the intensity of the radiation is decreased as it passes through the material.
How Lead Aprons Shield the Body
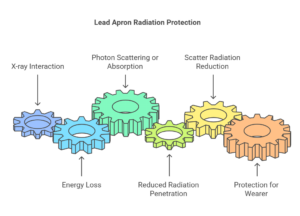
Absorption and Attenuation of Radiation
The primary function of a lead apron is to absorb X-rays and prevent them from penetrating the body. The lead in the apron acts as a barrier, preventing the X-rays from reaching sensitive tissues and organs. The thickness of the lead and the density of the material determine how effectively the apron can block radiation. Typically, a lead apron consists of a lead equivalent thickness that ranges from 0.25 mm to 1 mm, depending on the type of radiation and the level of protection needed.
When X-rays come into contact with the lead apron, the photons of radiation interact with the electrons in the lead atoms. This interaction causes the X-ray photons to lose energy, either by being scattered or absorbed entirely by the lead. This process reduces the amount of radiation that continues through the apron, significantly lowering the exposure to the person wearing the protective gear.
Reducing Scatter Radiation
In addition to absorbing direct radiation, lead aprons also help to reduce scatter radiation. Scatter radiation occurs when X-rays bounce off the patient or surrounding surfaces, potentially exposing medical professionals or other individuals in the room to harmful radiation. By wearing a lead apron, healthcare workers are shielded from this indirect exposure. The apron serves as a barrier that absorbs scattered X-rays, preventing them from reaching the person wearing the apron.
The Importance of Wearing Lead Aprons in Medical Imaging
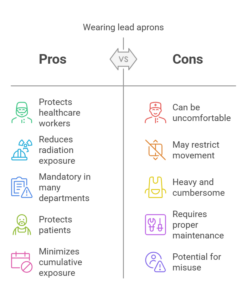
Protecting Medical Professionals
Healthcare workers who work in environments with frequent radiation exposure, such as radiologists, radiologic technologists, and surgeons, are at an increased risk of developing radiation-related health issues. By wearing lead aprons, these professionals significantly reduce their risk of exposure. Lead aprons are especially critical during procedures that involve prolonged radiation exposure, such as fluoroscopy or interventional radiology.
In many medical imaging departments, lead aprons are considered mandatory protective gear for professionals working near X-ray machines or other radiation-emitting equipment. The consistent use of lead aprons helps to minimize the cumulative radiation exposure that healthcare workers may accumulate over time, ensuring their safety and long-term health.
Protecting Patients
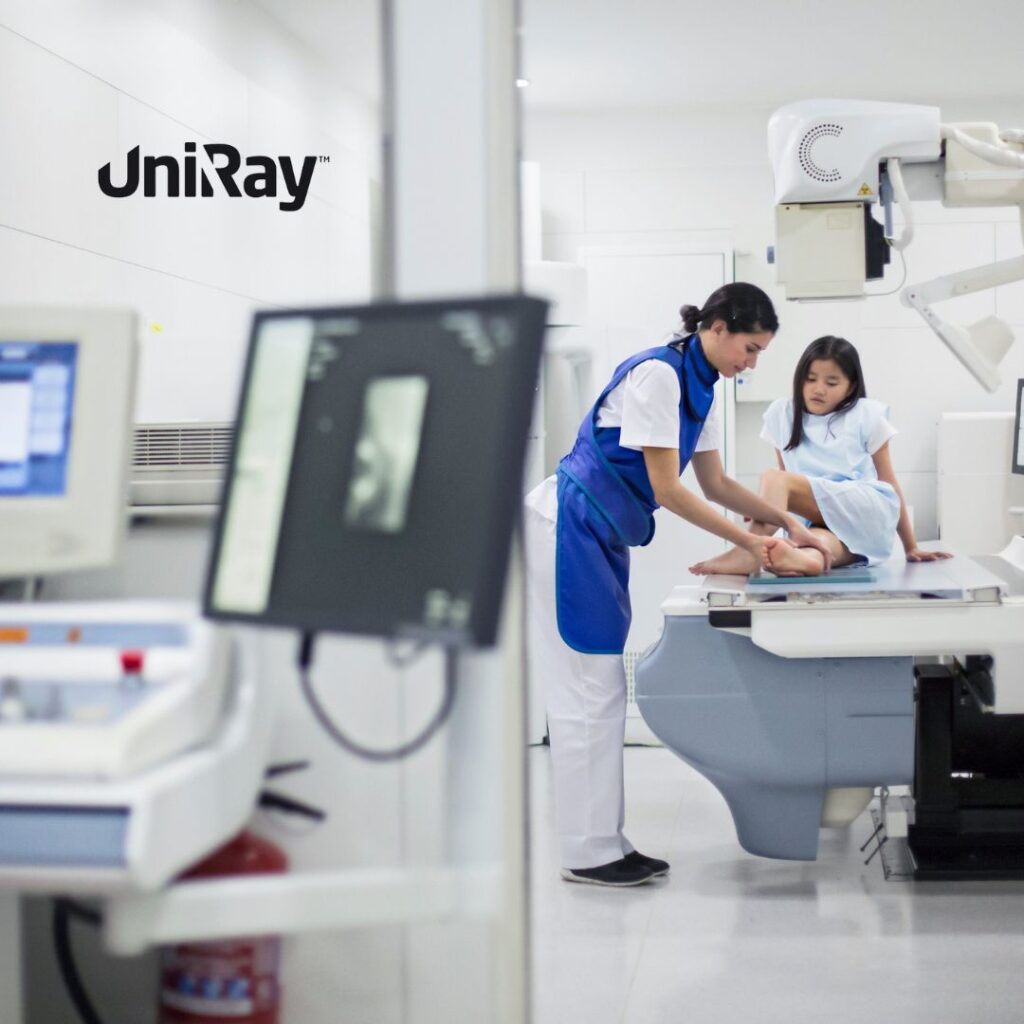
While the primary purpose of lead aprons is to protect medical professionals, they also play a crucial role in protecting patients from unnecessary radiation exposure. In procedures where radiation is directed toward a specific area of the body, such as X-ray imaging or CT scans, lead aprons are used to shield parts of the body that are not being imaged. For example, lead aprons may cover a patient’s abdomen or pelvis during chest X-rays, protecting vital organs from excessive radiation.
Patients, especially pregnant women and young children, are particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of radiation. By using lead aprons, healthcare providers can ensure that the benefits of medical imaging far outweigh the risks, minimizing the potential harm caused by radiation exposure.
Other Protective Gear in Medical Imaging: Thyroid Shields and More

While lead aprons are essential for overall radiation protection, they are not the only piece of protective gear used in medical imaging. Other devices, such as thyroid shields, are equally important in safeguarding sensitive areas of the body.
The Role of Thyroid Shields
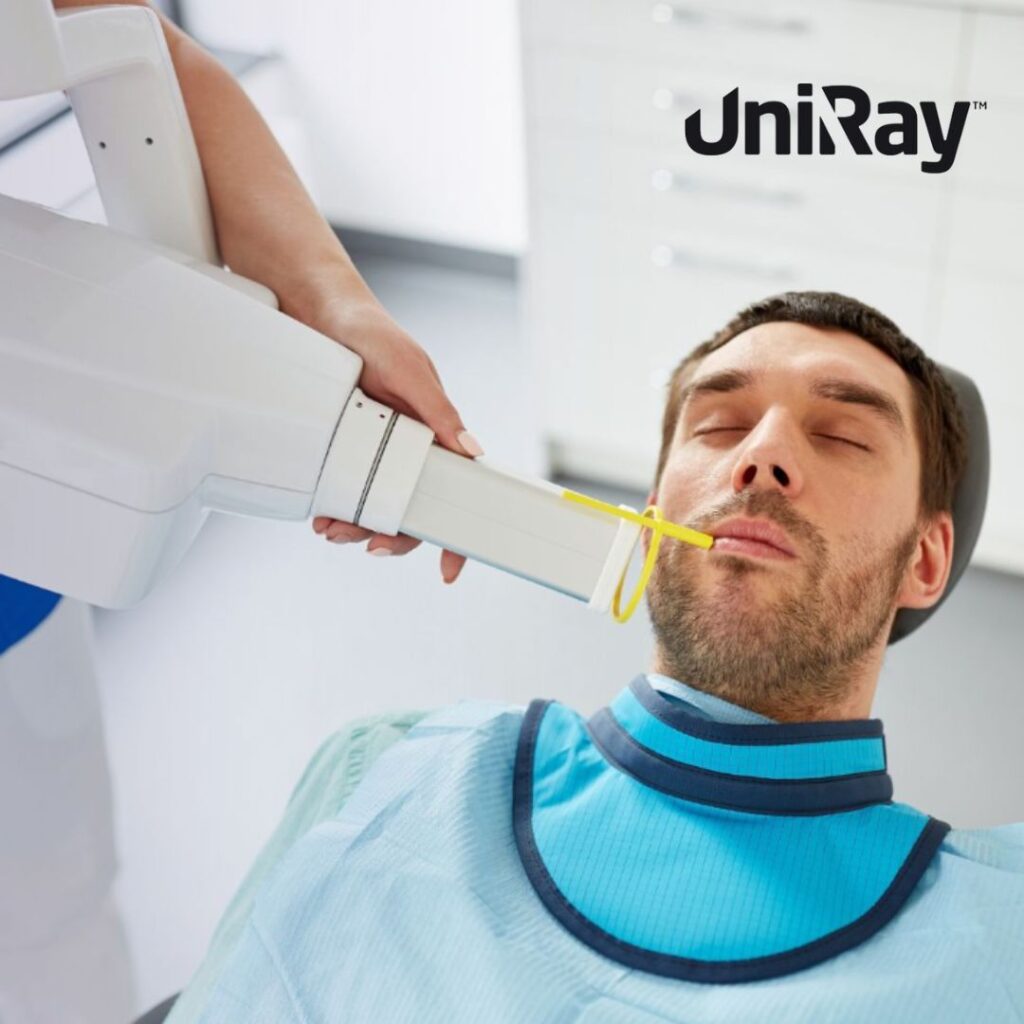
The thyroid gland is one of the most sensitive organs when it comes to radiation exposure. The thyroid is highly susceptible to radiation-induced damage, which can lead to conditions like thyroid cancer or hypothyroidism. Because of this, medical professionals and patients alike often wear thyroid shields during imaging procedures that involve radiation.
Thyroid shields are typically made from a combination of lead and other protective materials and are worn around the neck to cover the thyroid gland. These shields offer an extra layer of protection for this delicate area of the body, ensuring that radiation exposure is minimized. In many cases, wearing a thyroid shield is considered an essential part of radiation safety protocols, especially when the radiation dose is high or the procedure involves prolonged exposure.
The Importance of Proper Positioning and Additional Protective Measures
In addition to wearing lead aprons and thyroid shields, proper positioning during medical imaging procedures is critical in ensuring safety. For example, patients may be asked to adjust their position to ensure that only the area requiring imaging is exposed to radiation. By minimizing the exposed area, healthcare providers can reduce unnecessary radiation exposure to surrounding tissues.
In some cases, additional protective measures, such as lead gloves, lead glasses, and lead collars, may be used to further reduce the risk of radiation exposure. These items provide added protection for specific areas of the body that may be more vulnerable to radiation, such as the hands, eyes, and neck.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Lead Aprons in Radiation Protection
Lead aprons are indispensable tools in the field of medical imaging, providing a reliable and effective means of protecting both patients and healthcare professionals from harmful radiation exposure. By absorbing and attenuating X-ray apron, lead aprons significantly reduce the risk of radiation-related health issues, such as cancer and tissue damage. Additionally, when used in conjunction with other protective gear, such as thyroid collar, lead aprons help ensure the safety and well-being of everyone involved in medical imaging procedures.
Understanding how lead aprons stop radiation and why they are so essential in medical imaging is key to ensuring their proper use. As technology continues to advance, ongoing research and innovation will further enhance radiation protection, but for now, lead aprons remain a critical component of radiation safety. Whether you’re a healthcare worker or a patient undergoing imaging, always remember that proper protection, such as wearing a thyroid shield and lead apron, is your best defense against the risks of radiation exposure.
For additional protection, consider using a thyroid shield when undergoing imaging procedures that involve radiation, especially for sensitive areas like the neck and throat.