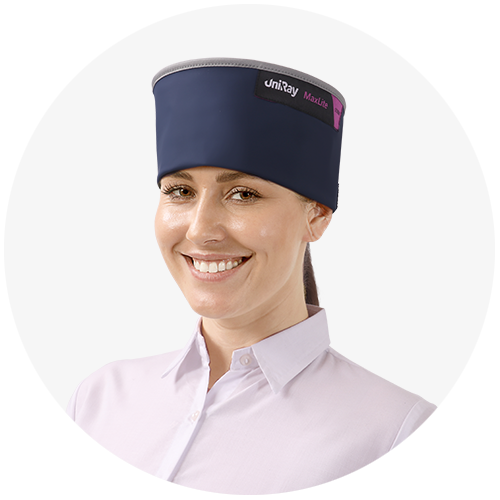
OUR APPAREL RANGE
UniRayTM offers a complete range of radiation protection products in Germany, including Lead Apron and Lead Free Apron, designed to deliver exceptional function and style. Crafted with precision, our aprons cater to the needs of medical professionals and patients, offering maximum shielding against harmful radiation exposure without compromising mobility..
Beyond protection, UniRay™ prioritizes innovation and ergonomic design, making our radiology lead aprons, X-ray aprons, and patient X-ray protection aprons ideal for prolonged use in hospitals, dental clinics, imaging centers, and other medical settings. Whether you require traditional radiation protection products or advanced lightweight alternatives, UniRay™ delivers reliability, safety, and functionality tailored to modern healthcare demands.
Lead Apron vs. Lead Free Apron: Which is Right for You?
When it comes to radiation protection, both lead apron and lead-free apron are essential for shielding against harmful exposure. Traditionally, X-ray aprons made with a layer of lead have been the gold standard due to their effectiveness in patient X-ray protection apron usage, effectively blocking radiation. However, lead-free X-ray aprons are gaining popularity as a lighter and more eco-friendly option. These leadfree aprons, made from composite materials like tungsten or bismuth, offer similar levels of X-ray protection while reducing weight and environmental impact.
For enhanced protection, options like a coat apron, double-sided apron, or thyroid shield may be used, depending on the application. Additionally, radiation protection gloves and Dental lead apron ensure further safety for healthcare workers. Whether choosing a skirt & vest apron or full-body styles, the decision often comes down to factors like comfort, weight, and specific protection needs within your suite of radiation protection products.
People Also Ask
1. What is a lead apron used for?
A lead apron is a protective garment worn by patients and medical professionals during X-rays or other imaging procedures to shield the body from unnecessary radiation exposure. It is particularly effective in protecting sensitive organs and tissues, such as reproductive organs and the thyroid gland.
2. Where are lead aprons used?
Lead aprons are commonly used in medical and dental settings, including:
- Radiology departments (X-rays, CT scans, fluoroscopy)
- Dental clinics (dental X-rays)
- Cath labs (cardiac catheterization procedures)
- Operating rooms (during imaging-guided surgeries)
3. What are the rules for lead apron?
- Proper Fit: The apron must fit the wearer correctly to ensure full coverage of sensitive areas.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect aprons for cracks, tears, or wear that could compromise their effectiveness.
- Storage: Hang aprons on proper hangers to prevent damage; avoid folding or creasing.
- Usage: Ensure aprons are worn during all procedures involving ionizing radiation.
- Replacement: Replace aprons if they show signs of damage or wear.
4. What is lead apron in cath?
In cardiac catheterization (cath) labs, lead aprons are worn by medical staff and sometimes patients to protect against radiation exposure during procedures like angiography or stent placement. These procedures involve prolonged use of fluoroscopy, which emits continuous radiation.
5. What material can block radiation?
Materials that can block radiation include:
- Lead: Highly effective for blocking X-rays and gamma rays.
- Concrete: Used in construction of radiation shielding walls.
- Tungsten: Often used as an alternative to lead in medical and industrial applications.
- Bismuth: Used in lightweight radiation shielding garments.
6. What is the best protection for radiation?
The best protection depends on the type and intensity of radiation. Common methods include:
- Lead aprons and shields: For medical and dental X-rays.
- Thick concrete or lead-lined walls: For nuclear facilities.
- Distance and time: Minimizing exposure time and maximizing distance from the radiation source.
7. Which chemical is used for radiation protection?
- Potassium iodide (KI): Used to protect the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine in nuclear emergencies.
- Prussian blue: Used to treat internal contamination with radioactive cesium or thallium.
8. What is used for radiation protection?
- Protective clothing: Lead aprons, thyroid shields, and glove surgery.
- Shielding materials: Lead, concrete, and tungsten.
- Monitoring devices: Dosimeters to measure radiation exposure.
9. What is a lead-free apron?
A lead-free apron is a radiation protection garment made from alternative materials like bismuth, antimony, or tungsten. These aprons provide similar protection to lead aprons but are lighter and more environmentally friendly.
10. What is the difference between lead and non-lead aprons?
- Weight: Non-lead aprons are lighter and more comfortable to wear.
- Material: Lead aprons contain lead, while non-lead aprons use materials like bismuth or tungsten.
- Environmental impact: Non-lead aprons are more eco-friendly and easier to dispose of.
- Protection: Both provide similar levels of radiation protection when designed properly.
11. Are lead aprons safe?
Yes, lead aprons are safe when used correctly. They are designed to shield the body from radiation, and the lead is encapsulated in protective layers to prevent direct contact. However, improper handling or damage to the apron can reduce its effectiveness.
12. Why are lead aprons no longer recommended?
Lead aprons are being phased out in some settings due to:
- Environmental concerns: Lead is toxic and poses disposal challenges.
- Weight: Lead aprons are heavy and can cause discomfort or injury over time.
- Advancements in technology: Non-lead alternatives offer comparable protection with added benefits like reduced weight and improved ergonomics.