Radiation protection is critical in safeguarding individuals and the environment from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation. Whether working in medical imaging, industrial applications, or nuclear facilities, understanding and adhering to established radiation protection guidelines is essential for minimizing risks and ensuring safety.
What Is Radiation Protection?
Radiation protection involves measures to control exposure to ionizing radiation, ensuring safety for workers, patients, and the public. The goal is to minimize radiation doses and prevent radiation-related hazards while maximizing its beneficial uses in medicine, industry, and research.
Principles of Radiation Protection
The foundation of radiation protection relies on three primary principles:
- Justification
- Every radiation exposure must have a clear benefit outweighing the risks.
- Example: Using X-rays in medical diagnostics only when necessary for accurate diagnosis.
- Optimization (ALARA Principle)
- Stands for “As Low As Reasonably Achievable.”
- Optimize procedures and equipment to reduce radiation exposure to the lowest possible levels.
- Dose Limitation
- Establishing dose limits for occupational workers, patients, and the public.
- These limits are based on guidelines from international organizations like the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP).
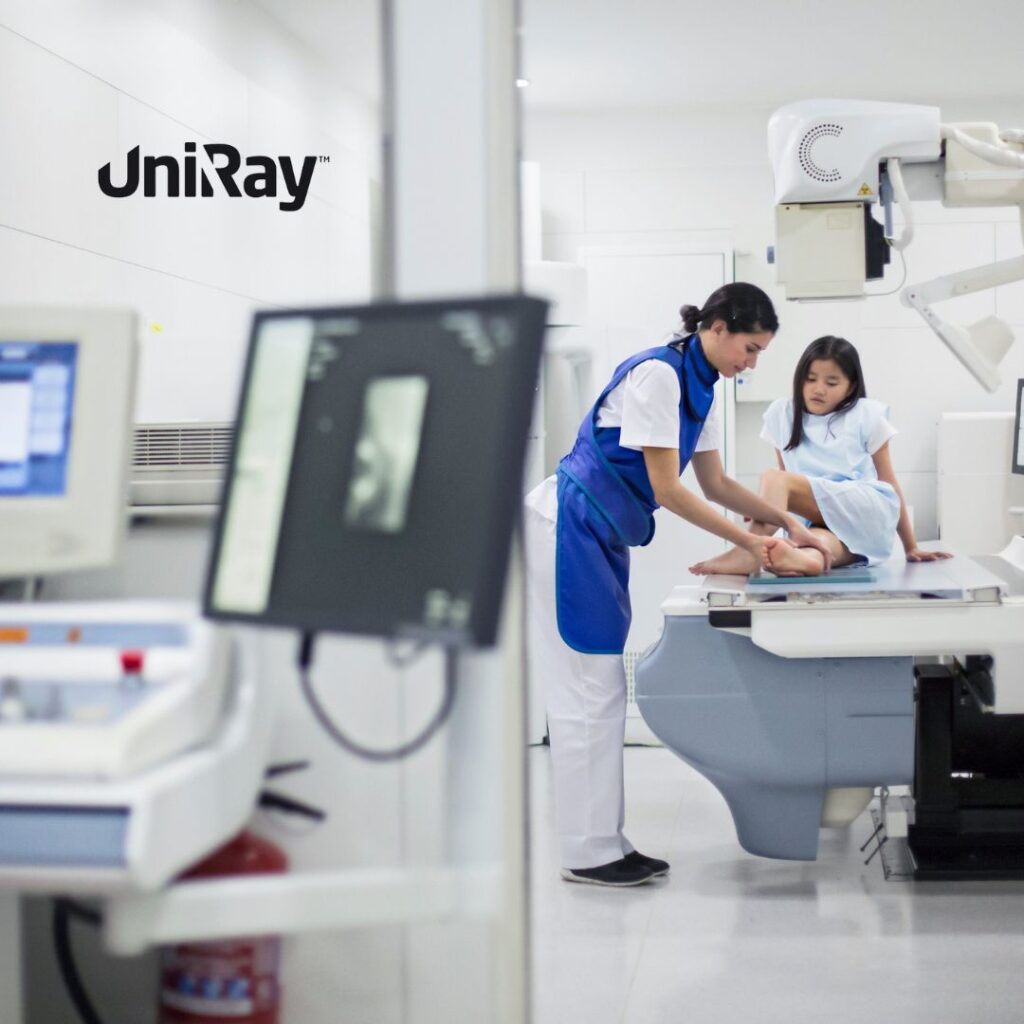
Radiation Protection Guidelines in Healthcare
Healthcare professionals are among the most exposed to radiation, especially in diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment. Specific guidelines ensure their safety while delivering effective care:
- Protective Equipment
- Use lead apron, thyroid shield, and radiation protection gloves during procedures.
- Ensure regular maintenance and quality checks of protective gear.
- Controlled Areas
- Designate areas with restricted access where radiation levels are high.
- Display warning signs and ensure proper shielding in these zones.
- Time, Distance, and Shielding
- Time: Minimize the duration of exposure.
- Distance: Maintain a safe distance from radiation sources.
- Shielding: Use barriers like lead walls and protective screens.
- Regular Monitoring
- Use dosimeters to track radiation exposure levels of healthcare workers.
- Conduct routine audits to ensure compliance with radiation protection and safety standards.
Radiation Protection and Safety in Industrial Applications
Industries using radiation for purposes such as material testing, sterilization, or energy production must follow stringent safety protocols:
- Training and Certification
- Ensure all personnel handling radiation sources are adequately trained.
- Provide periodic refresher courses to stay updated with evolving guidelines.
- Safety Protocols
- Regularly inspect equipment for leaks or malfunctions.
- Implement emergency response procedures for accidental exposure.
- Radiation Safety Officers (RSOs)
- Appoint qualified professionals to oversee radiation protection programs.
- RSOs are responsible for monitoring radiation levels and ensuring regulatory compliance.
International Guidelines for Radiation Protection
Several organizations provide comprehensive frameworks for radiation safety. These include:
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Sets global safety standards for radiation protection.
- World Health Organization (WHO): Offers guidelines for medical radiation use.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): Regulates workplace radiation safety in the U.S.
Guidelines for Radiation Protection at Home
While most radiation exposure occurs in professional or medical settings, minimal exposure at home can arise from natural sources like radon gas or electronic devices.
- Radon Testing: Test your home for radon levels, especially in basements.
- Safe Usage of Electronics: Avoid prolonged exposure to devices emitting low-level radiation, like microwaves.
- Protective Measures for Pregnant Women: Avoid unnecessary X-rays during pregnancy to safeguard the unborn child.
Emerging Technologies in Radiation Protection
Advances in technology continue to improve radiation safety.
- Wearable Radiation Monitors: Provide real-time exposure tracking for workers.
- Automated Systems: Robotics and AI minimize human involvement in high-radiation tasks.
- Innovative Shielding Materials: New composites offer better protection with reduced weight and bulk.
Why Adhering to Radiation Protection Guidelines Is Critical
Neglecting radiation safety can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Health Risks: Increased chances of cancer, burns, or radiation sickness.
- Environmental Hazards: Contamination of air, water, and soil.
- Legal and Financial Implications: Penalties for failing to comply with regulatory standards.
By implementing robust radiation protection and safety measures, industries and healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of workers, patients, and the public while maintaining operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Radiation plays a vital role in advancing technology, healthcare, and industry. However, adhering to established guidelines for radiation protection is non-negotiable to minimize risks and maximize benefits. From healthcare facilities to industrial plants and even households, understanding and applying these principles ensure a safer environment for everyone.
Ready to take action? Start implementing these radiation protection guidelines today to secure a safer tomorrow.
Would you like assistance with optimizing specific sections or incorporating more technical details?