The Importance of Medical Radiation Shielding: Protecting Health and Enhancing Safety
In modern medical practices, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures often involve exposure to ionising radiation. While radiation is a powerful tool for imaging and treatment, it poses serious health risks when safety precautions are not taken. This is where medical radiation shielding plays a crucial role. With rising use of X-rays, CT scans, and radiation therapy, the need for reliable protective measures has never been greater. One such essential protection gear includes radioactive glasses, which help reduce radiation exposure to the eyes, one of the most sensitive organs.
Understanding Medical Radiation Shielding
Medical radiation shielding refers to the use of materials and barriers to protect patients and medical professionals from unnecessary exposure to ionising radiation. These materials, often made of lead or lead alternatives, absorb or block radiation from reaching vital body parts. Radiation shielding is essential in hospitals, dental clinics, diagnostic imaging centres, and radiotherapy units.
The need for shielding stems from the biological effects of radiation exposure. Ionising radiation can damage DNA, increase cancer risks, and cause acute radiation syndromes in high doses. Shielding helps to mitigate these risks by creating physical barriers between radiation sources and people.
Types of Radiation Used in Healthcare
Understanding the types of radiation used in healthcare can help us comprehend the importance of shielding:
X-rays – Used in diagnostic radiology, including general X-rays and mammography.
Gamma rays – Used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Beta particles and other ionising particles – Found in some specific treatment protocols.
Proton and heavy ion therapy – Advanced cancer treatment methods using high-energy particles.
These various forms of radiation have different penetration levels, making it essential to choose the right shielding equipment depending on the procedure.
Shielding Materials: The Front Line of Defence
The effectiveness of medical radiation shielding depends significantly on the materials used. Commonly used materials include:
Lead: Known for its high density, lead is the gold standard in radiation shielding. It effectively blocks X-rays and gamma rays.
Lead-free composites: These materials are lighter and more eco-friendly while still offering considerable radiation protection.
Tungsten and bismuth: Used in certain applications where weight and flexibility matter.
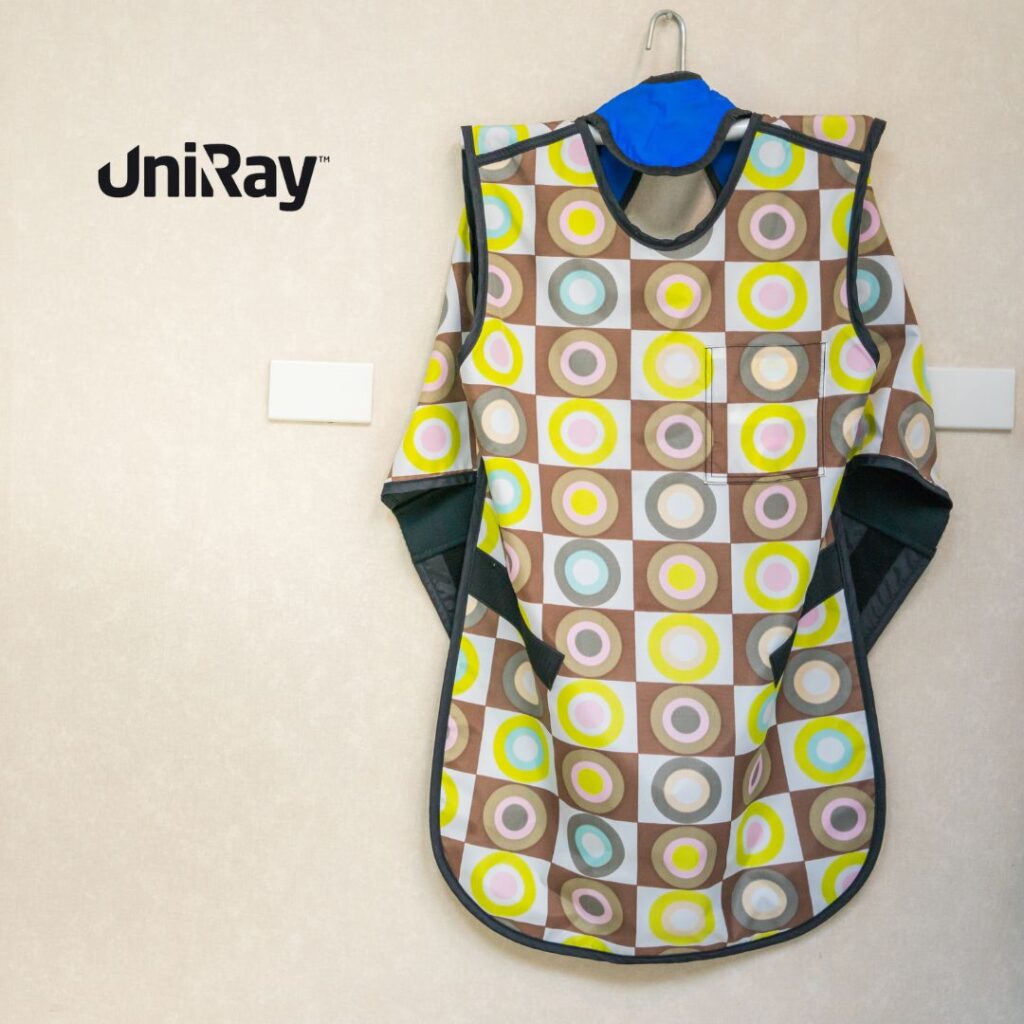
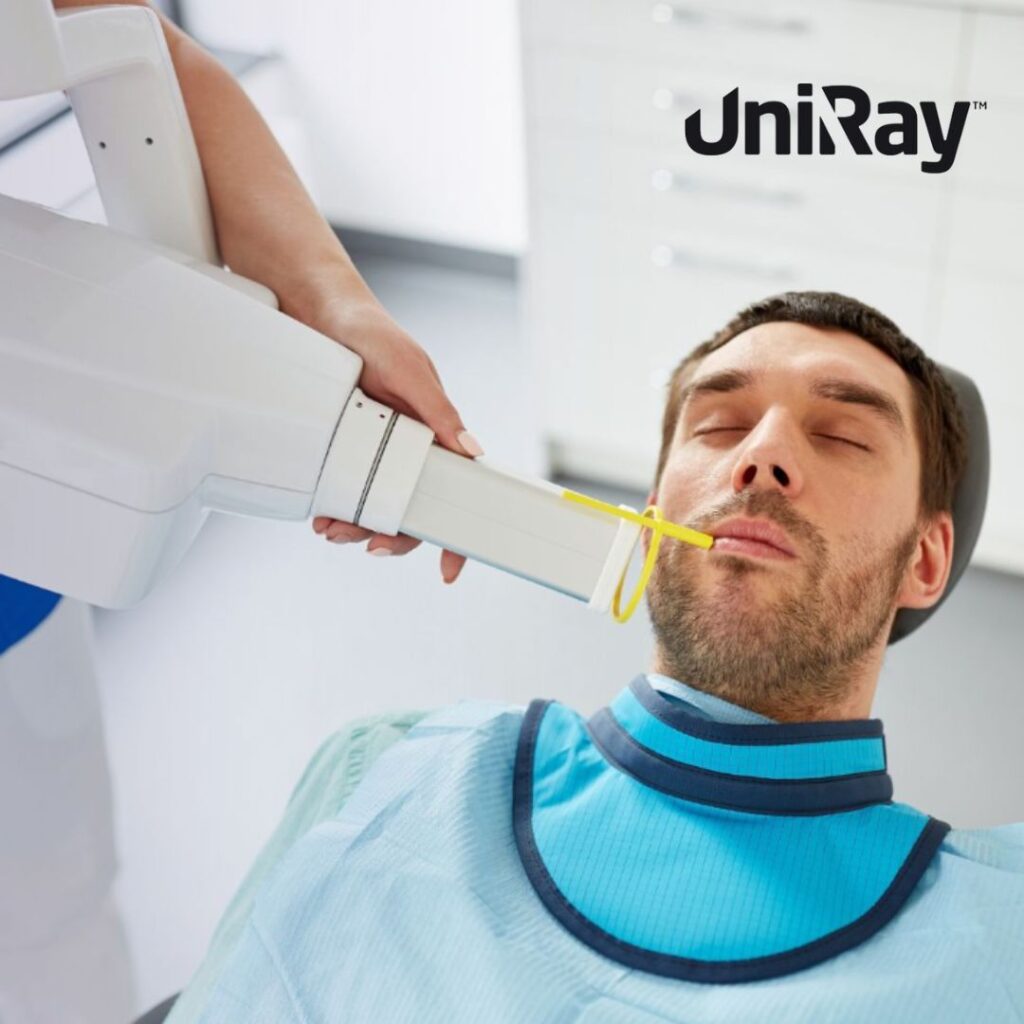
Shielding can be applied in walls, windows, doors, mobile barriers, and personal protective equipment (PPE) such as aprons, thyroid shields, gloves, and eyewear.
One of the most frequently used protective items in radiology rooms is the Lead Apron, which significantly reduces exposure to the chest and abdomen.
Common Areas Requiring Medical Radiation Shielding
Various areas in medical facilities need comprehensive shielding solutions:
Radiology and fluoroscopy rooms
CT scan and MRI suites
Nuclear medicine labs
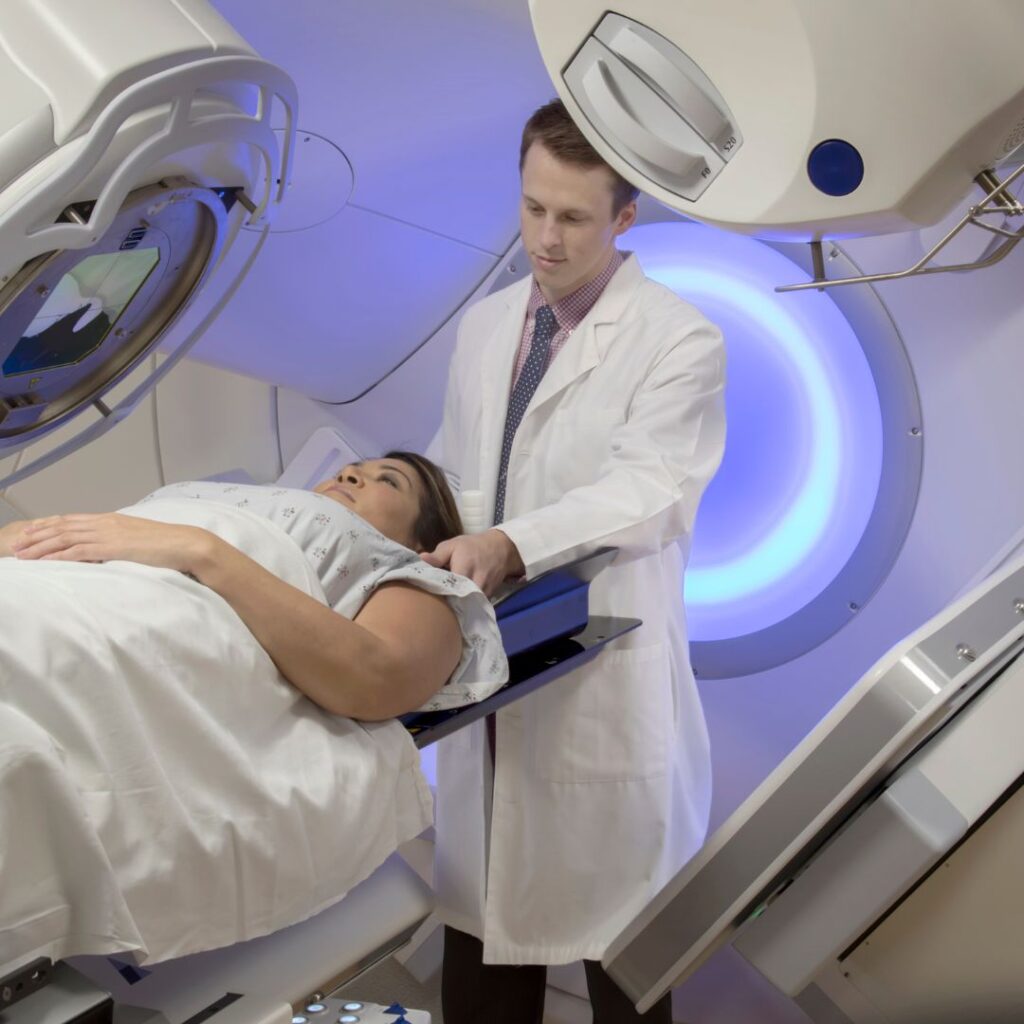
Radiotherapy rooms
Operating theatres using intraoperative imaging
In these environments, walls and floors may be lined with shielding materials, and professionals are equipped with personal protection to ensure cumulative exposure remains within safe limits.
How Shielding Protects Medical Professionals and Patients
Professionals who work with radiation daily, such as radiologists and technicians, are at higher risk of cumulative exposure. Without adequate shielding, they can face serious long-term health issues, including cancer and cataracts.
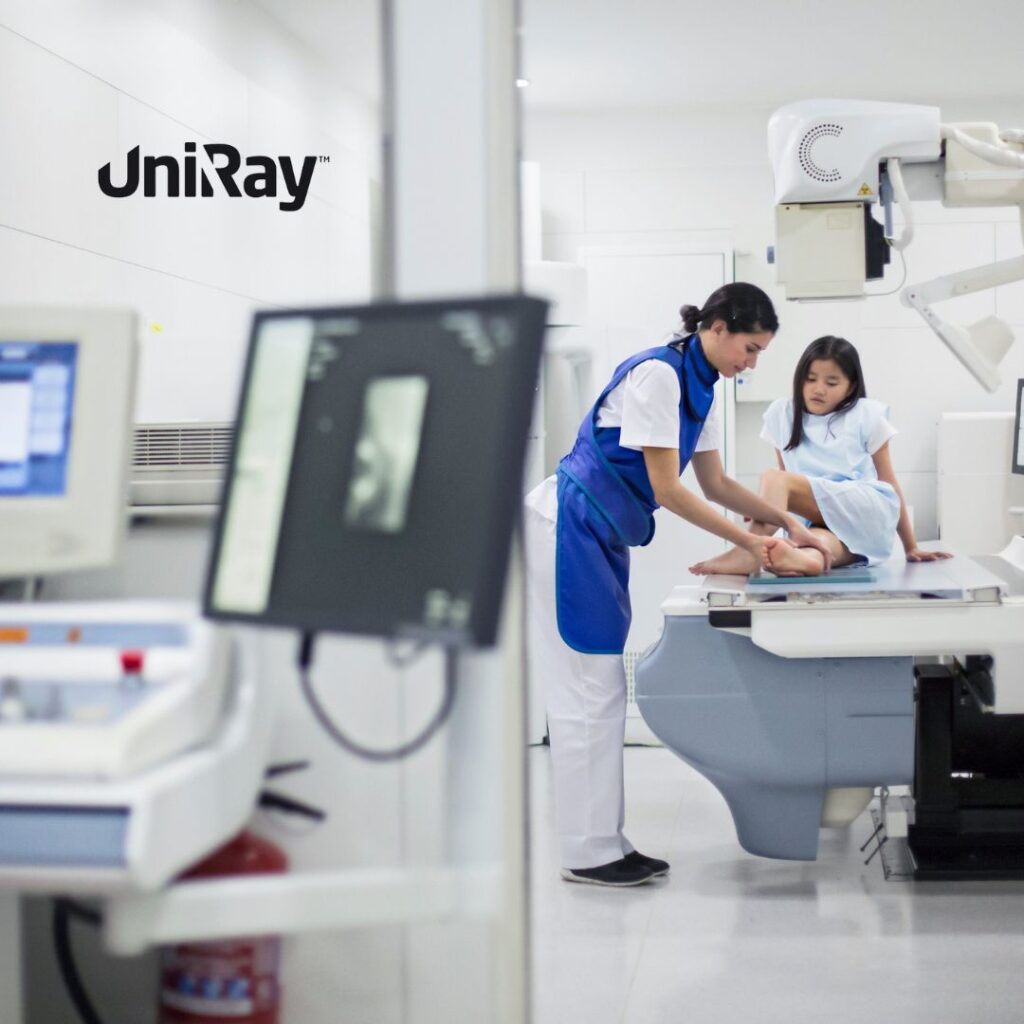
Patients, though exposed less frequently, are still at risk during diagnostic imaging and treatment. Children, pregnant women, and individuals requiring repeated imaging are especially vulnerable.
Shielding ensures that radiation is focused only on the target area, thereby reducing unnecessary exposure to surrounding tissues. Technologies such as beam collimators and software controls further enhance precision, but physical shielding remains indispensable.
Innovations in Medical Radiation Shielding
The medical field has witnessed significant innovation in radiation protection over the past decade. Modern shielding is designed to be lightweight, flexible, and more comfortable without compromising effectiveness. For instance, protective wear now includes ergonomic features, breathable fabrics, and improved adjustability.
Moreover, modular room shields and mobile barriers provide flexibility and mobility, allowing hospitals to adapt shielding as per their spatial layout. Also, smart shielding devices are being developed with embedded sensors to measure real-time radiation exposure.
Training and Safety Protocols
Having advanced shielding equipment is only part of the solution. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are equally vital. All healthcare staff working with radiation must undergo regular training on:
Proper usage of protective equipment
Understanding dose limits
Handling emergencies
Safe positioning during procedures
Regular audits and inspections ensure that shielding installations remain effective and equipment is up to standard. Hospital management must also invest in ongoing education to reinforce a culture of radiation safety.
Role of Safety Shielding in CT Imaging
CT scans are one of the highest sources of radiation exposure in diagnostics. The demand for clear imaging makes it essential to balance image quality and patient safety. Innovations in safety shielding have significantly improved outcomes in CT imaging.
CT shields such as bismuth breast shields, thyroid collars, and paediatric eye shields reduce the dose delivered to sensitive tissues without affecting the diagnostic value of the image. These shields are especially important for patients requiring frequent scans or children undergoing diagnostic tests.
Future Trends in Radiation Shielding
The future of medical radiation shielding looks promising with trends such as:
Nanotechnology: Used to develop lightweight and highly effective shielding materials.
Custom-fit PPE: 3D scanning and printing used to create personalised shielding gear.
Smart textiles: Wearable shielding integrated with sensors to monitor radiation levels.
Eco-friendly materials: Development of lead-free shields that are safer for both users and the environment.
As medical procedures become more complex and technology-driven, the demand for advanced radiation protection will continue to grow.
Final Thoughts
Medical radiation shielding is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a vital component of patient and staff safety in modern healthcare. From radioactive glasses and Lead Aprons to sophisticated safety shielding, each element plays a key role in reducing exposure and ensuring safe medical practices. As technology advances, so too must our commitment to radiation safety—because in healthcare, prevention is always better than cure.