Radiation protection is an essential consideration in medical, dental, and radiological practices. Among the many protective measures available, the thyroid collar stands out as a critical tool to safeguard the thyroid gland from radiation exposure. This blog will delve into the uses of a thyroid collar, its importance in various fields, and how it contributes to overall health safety.
What Is a Thyroid Collar?
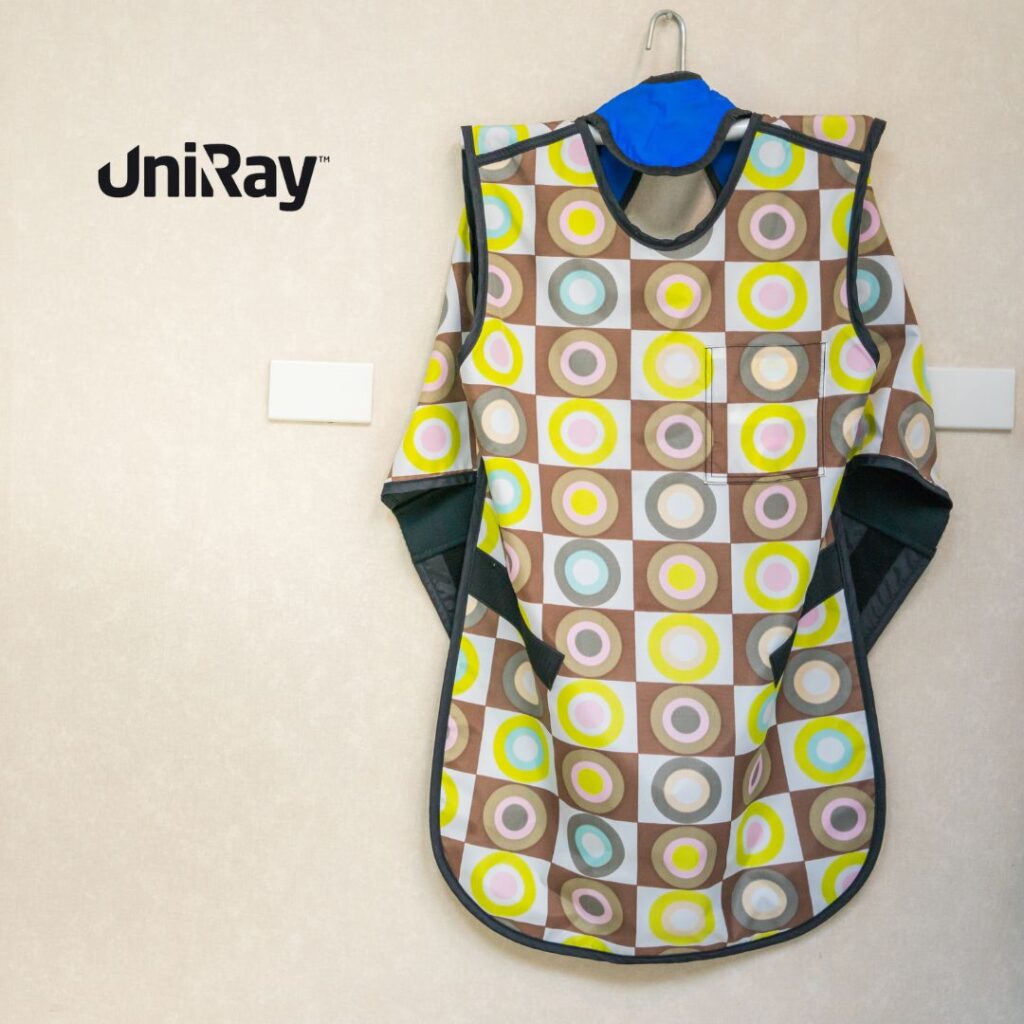
A thyroid shield or collar is a specialized piece of protective equipment designed to shield the thyroid gland from radiation. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and hormone production. Its sensitivity to radiation makes it particularly vulnerable, and even low levels of exposure can lead to long-term health consequences.
Why Is the Thyroid Gland Vulnerable to Radiation?
The thyroid gland is highly sensitive because of its rapid cellular turnover and iodine absorption capacity. When exposed to ionizing radiation, the gland faces an increased risk of damage, which may lead to conditions such as thyroid cancer, hypothyroidism, or other endocrine disorders. This makes protection imperative in environments where radiation exposure is possible.
Sources of Radiation in Medical and Dental Settings
- X-rays: Commonly used in dental and medical imaging.
- CT scans: Involve higher doses of radiation compared to standard X-rays.
- Fluoroscopy: Used during interventional procedures and involves prolonged radiation exposure.
- Radiation therapy: Targeted treatments for cancer often expose surrounding tissues to radiation.
Uses of a Thyroid Collar
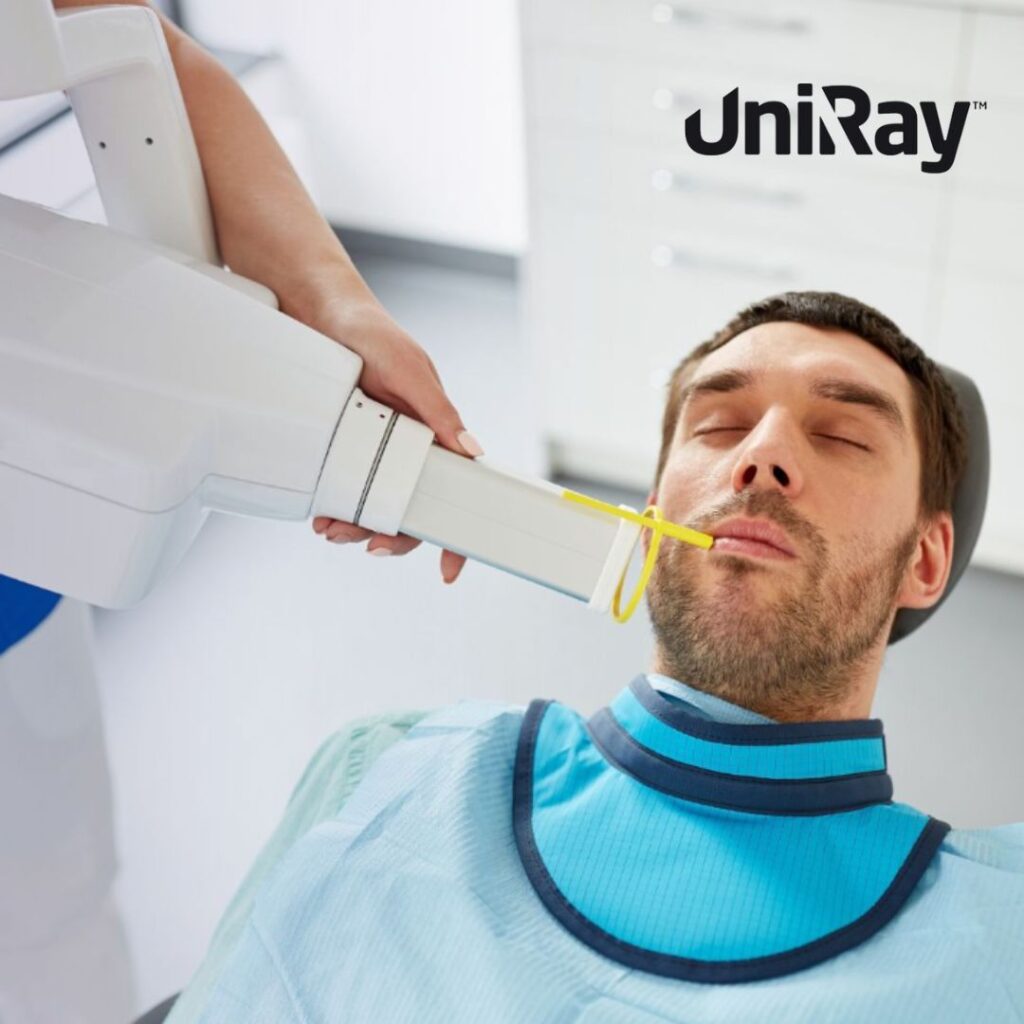
1. Dental Radiography
One of the most common uses of a thyroid collar is in dental imaging. Dentists often recommend X-rays to diagnose cavities, check bone density, or assess the alignment of teeth. During these procedures, a thyroid collar is placed around the neck to prevent stray radiation from affecting the thyroid gland.
2. Medical Imaging Procedures
In medical settings, thyroid collars are essential during diagnostic imaging, such as CT scans or fluoroscopy, particularly when the neck area is not the primary focus of imaging. Using a thyroid collar minimizes the risk of scatter radiation.
3. Radiation Therapy
For patients undergoing radiation therapy for cancers in areas other than the thyroid, protective equipment like thyroid collars is used to shield the gland from incidental exposure. This ensures that the treatment targets the diseased area while sparing the thyroid.
4. Veterinary Practices
Radiation safety extends beyond human care. In veterinary settings, thyroid collars are used when imaging or treating animals to protect handlers and minimize exposure risks.
5. Educational and Research Institutions
Laboratories and research facilities that involve radiation-based experiments employ thyroid collars to protect staff and researchers.
Benefits of Using a Thyroid Collar
1. Prevents Long-term Health Risks
The thyroid gland’s exposure to radiation is a known risk factor for developing thyroid cancer. By using a thyroid collar, these risks are significantly reduced.
2. Enhances Patient Safety
Patients undergoing repeated imaging procedures, such as those with chronic illnesses, benefit from added safety measures like thyroid collars, which lower cumulative radiation exposure.
3. Mandatory in Regulatory Compliance
Many regulatory bodies mandate the use of protective equipment, including thyroid collars, in radiation-related procedures. Compliance ensures both legal and ethical standards are met.
Materials and Design of Thyroid Collars
Thyroid collars are typically made from lead or lead-free materials designed to absorb radiation.
1. Lead Thyroid Collars
- Offer excellent radiation protection.
- Heavier but highly effective.
2. Lead-free Thyroid Collars
- Made from materials like bismuth or antimony.
- Lightweight and eco-friendly.
3. Adjustable and Ergonomic Designs
Modern thyroid collars are designed for comfort and efficiency, featuring adjustable straps and ergonomic shapes to suit all neck sizes.
How to Use a Thyroid Collar Correctly
Proper use is critical to ensuring maximum protection.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Place the collar snugly around the neck, ensuring full coverage of the thyroid gland.
- Adjust the straps for a secure but comfortable fit.
- Ensure there are no gaps where radiation might penetrate.
- Use the thyroid collar in conjunction with other protective gear, such as aprons or gloves, for comprehensive safety.
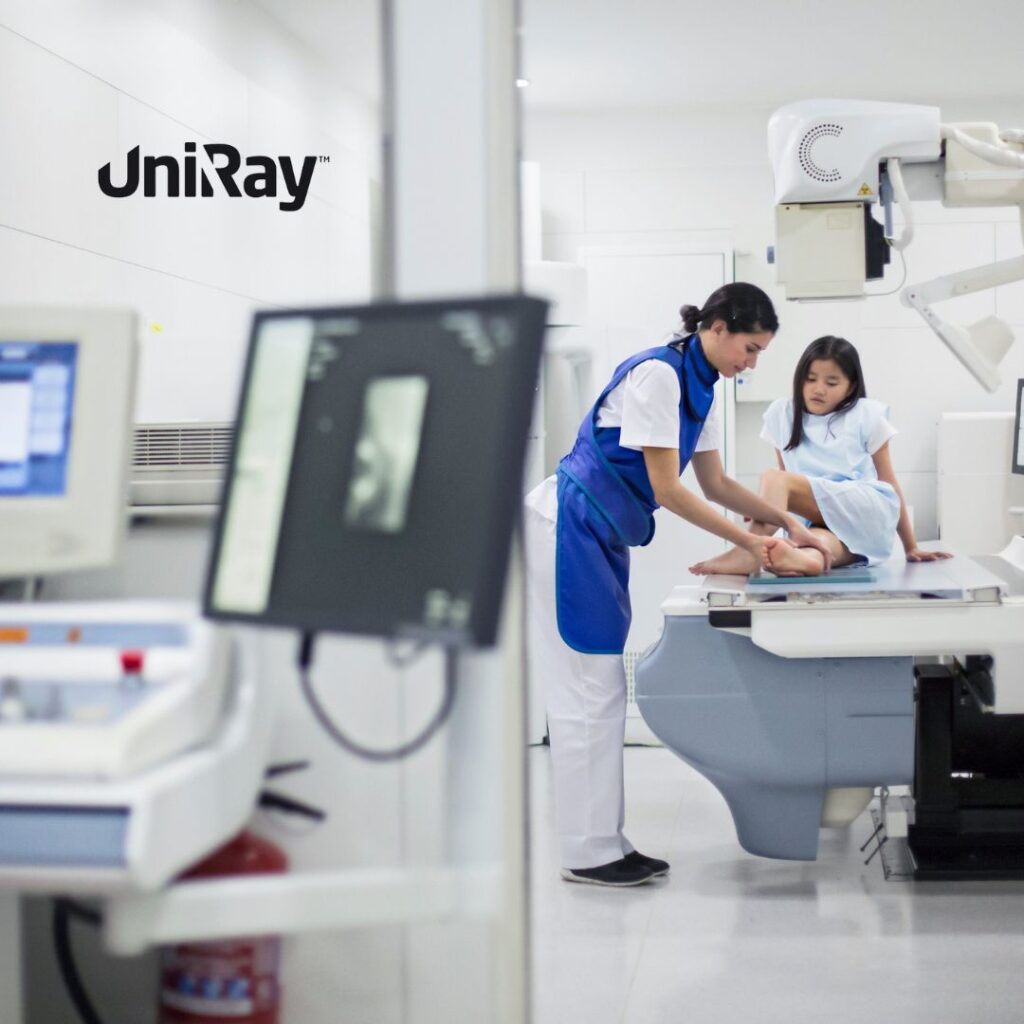
The Role of Thyroid Collars in Pediatric Care
Children are particularly susceptible to the harmful effects of radiation because their tissues are still developing. Pediatric imaging often involves thyroid collars to mitigate these risks and protect young patients from potential long-term consequences.
Maintenance and Care of Thyroid Collars
To ensure the longevity and effectiveness of a thyroid collar, proper maintenance is essential.
Cleaning and Storage
- Clean regularly with a damp cloth and mild detergent.
- Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Inspection and Replacement
- Inspect regularly for cracks, tears, or wear.
- Replace collars that show signs of damage to maintain optimal protection.
Conclusion
Lead apron and thyroid collars are indispensable in radiation protection, serving as vital barriers against potential health risks associated with radiation exposure. From dental radiography to medical imaging and beyond, their applications are diverse and critical. By understanding the uses and benefits of lead aprons and thyroid collars, as well as their proper maintenance, healthcare providers and patients alike can prioritize safety and minimize the long-term impact of radiation on the thyroid gland.
Investing in high-quality thyroid collars and ensuring their proper use can make a significant difference in safeguarding health, particularly in environments with frequent exposure to ionizing radiation.