Understanding Thyroid Shields and Their Importance
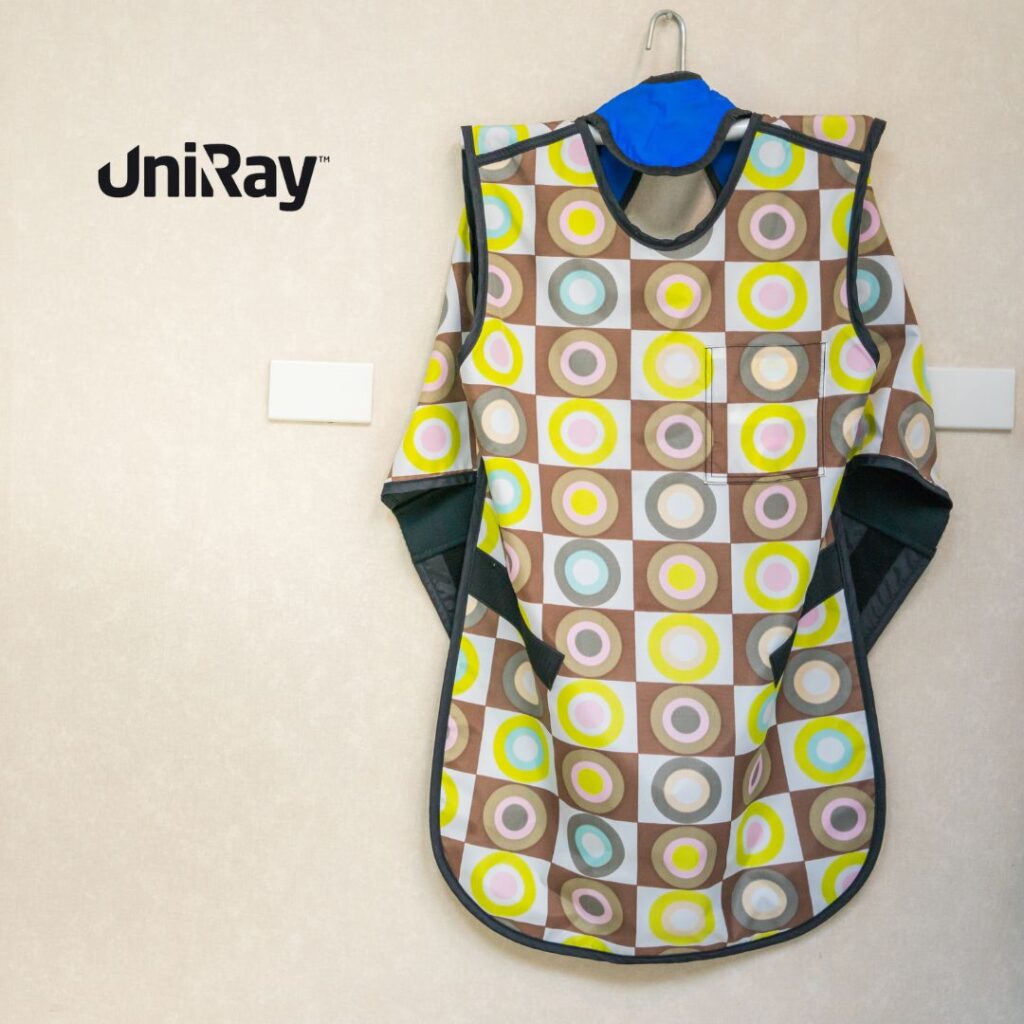
A thyroid shield, also called a lead thyroid collar or radiation shield, is an essential piece of protective gear used in medical and dental fields to guard the thyroid gland from harmful radiation exposure. Located in the neck, the thyroid gland is highly sensitive to radiation, and without adequate protection, even small doses can increase the risk of thyroid cancer and other radiation-related conditions. The thyroid shield is specifically designed to cover the neck area during X-rays, CT scans, and other diagnostic imaging procedures involving ionizing radiation, serving as a physical barrier between radiation sources and the thyroid. In radiation-sensitive environments, the thyroid shield is a key component of protective protocols for both healthcare providers and patients, significantly reducing cumulative radiation exposure. With various types, materials, and design advancements, the thyroid shield has evolved into an integral part of radiation safety practices, becoming essential for optimal patient and professional care.
How Thyroid Shields Function in Radiation Protection
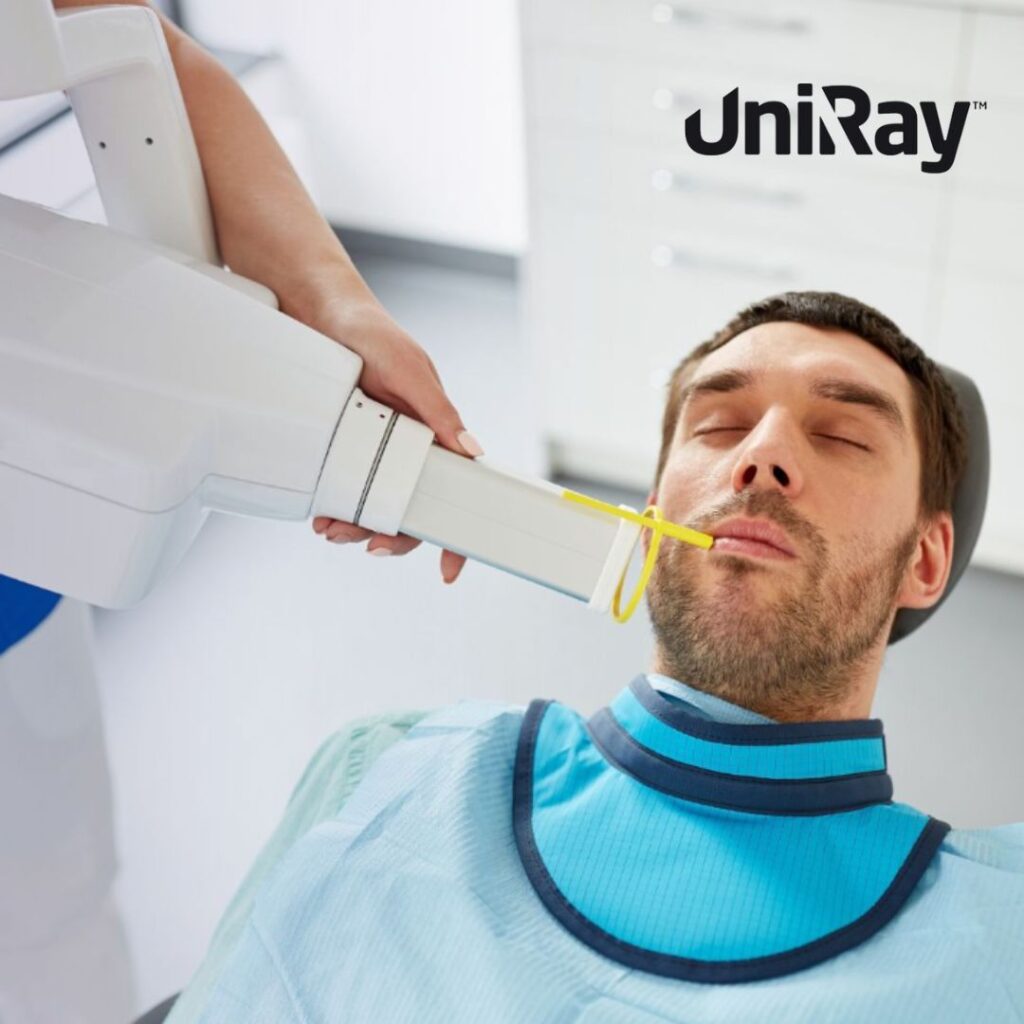
Thyroid shields work by creating a lead-based or lead-equivalent material barrier that absorbs radiation particles before they reach the thyroid gland. Lead is used due to its high density and effectiveness in blocking or absorbing ionizing radiation. The shields typically offer protection equivalent to 0.5mm of lead thickness, which is deemed adequate for most medical and dental imaging. The shield’s design allows for a snug fit around the neck, ensuring the thyroid gland remains shielded even when radiation is directed toward the head or chest. Different procedures can expose the thyroid to varying radiation levels, but wearing a thyroid shield is crucial regardless, as it prevents both direct and scattered radiation from reaching the thyroid. Especially in dental X-rays, where the radiation source is close to the neck, thyroid shields provide critical protection by reducing exposure to one of the body’s most radiation-sensitive glands.
Types of Thyroid Shields: Lead and Lead-Equivalent Options
Thyroid shields come in two main types: lead-based and lead-equivalent, with each offering unique advantages. Lead-based thyroid shields are effective but can be heavy and less comfortable, especially for long procedures. Lead-equivalent shields, however, are crafted from composite materials that provide the same level of radiation protection while being lighter and more flexible. These shields are becoming popular in healthcare settings where extended use is common. The lead-equivalent thyroid shields use a mix of barium, tungsten, or other metals to replicate lead’s protective qualities but with added comfort. The choice between lead and lead-equivalent shields often depends on the specific needs of the medical facility, frequency of shield use, and user comfort preferences. In settings where long-term use is anticipated, such as for dental hygienists and radiologists, lead-equivalent shields are ideal due to their durability and lighter weight, enhancing both protection and comfort without sacrificing safety standards.
Applications of Thyroid Shields in Medical and Dental Environments
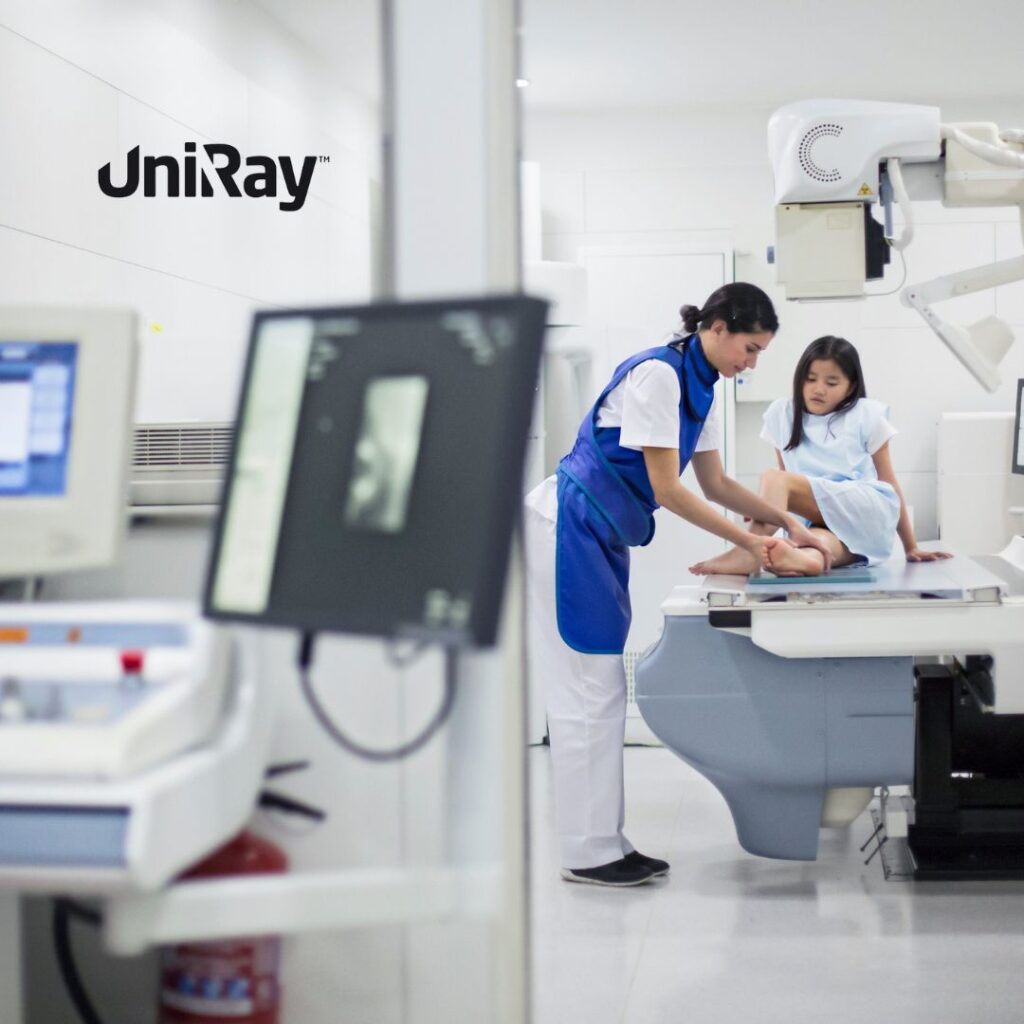
Thyroid shields are standard in environments where patients and healthcare professionals are exposed to radiation, including dental offices, hospitals, and radiology departments. In dental X-rays, thyroid shields are indispensable since the radiation source is near the thyroid gland, making it vulnerable to exposure. Shields are also widely used during CT scans, mammograms, and fluoroscopic procedures where ionizing radiation can scatter. Additionally, many healthcare providers in radiology, dentistry, and surgery use thyroid shields daily as part of their personal protective equipment. The shield protects professionals from cumulative radiation exposure, which can lead to health complications over time. Some facilities also use thyroid shields for patients undergoing frequent imaging procedures or in cases where the patient’s neck area is at risk of radiation exposure. This widespread use underscores the critical role thyroid shields play in enhancing radiation safety standards across medical and dental practices, providing essential protection against ionizing radiation for both patients and practitioners.
Correct Usage and Positioning of Thyroid Shields
For maximum protection, thyroid shields must be worn correctly, fitting snugly around the neck to fully cover the thyroid gland. The shield’s design allows it to be positioned comfortably while blocking both direct and scattered radiation. A properly fitted thyroid shield should not leave any gaps, as even minor exposure can impact thyroid health. Many shields are adjustable, allowing for a customized fit, which is particularly beneficial in busy medical settings with multiple patients. Healthcare providers should ensure that shields fit securely on patients before imaging procedures begin, as improperly positioned shields can reduce effectiveness. When in use, the shield should be checked for secure positioning to avoid shifts that could expose the thyroid. Consistent training for medical staff on the correct application of thyroid shields is essential to maintain high standards of patient safety, guaranteeing that every shielded procedure truly minimizes radiation exposure to the thyroid gland.
Impact of Thyroid Shields on Reducing Radiation-Related Health Risks
Radiation exposure can lead to various health issues, especially for sensitive organs like the thyroid. Studies have linked radiation exposure to an increased risk of thyroid cancer and other thyroid-related disorders, underscoring the importance of protection during diagnostic imaging. Even low doses of radiation can impact thyroid function over time, particularly in children and young adults, who have a higher risk of developing radiation-induced conditions. Regular use of thyroid shields is one of the most effective ways to reduce these risks, as the shields provide a physical barrier that minimizes exposure levels. By wearing thyroid shields, both patients and healthcare providers can protect themselves against potential long-term effects of radiation exposure, particularly in professions where imaging procedures are frequently performed. The reduction of radiation exposure through thyroid shields is consistent with the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle, which advocates for minimizing radiation doses wherever possible.
Maintenance and Care for Thyroid Shields
Maintaining thyroid shields in good condition is vital to ensure their effectiveness over time. Regular inspections for cracks, tears, or wear are essential, as any damage can compromise the shield’s ability to block radiation. In high-use settings like dental clinics, thyroid shields can experience frequent handling, making it crucial to inspect them consistently. Storage is also a key aspect of shield maintenance; thyroid shields should be stored flat or hung to prevent creasing, which can damage the lead or lead-equivalent material. Cleaning thyroid shields helps maintain hygiene, especially when used by multiple patients. Most manufacturers recommend mild soap and water for cleaning, avoiding harsh chemicals that could deteriorate the protective material. Proper care not only extends the life of the thyroid shield but also ensures continued protection, making regular maintenance a priority in healthcare facilities where radiation safety is essential.
Innovations in Thyroid Shield Technology
Advancements in medical technology have led to innovations in thyroid shield design and materials. Modern thyroid shields are now available in lightweight, lead-free versions that offer the same level of protection as traditional lead shields but with improved comfort and flexibility. Lead-free shields use materials like tungsten and barium to replicate lead’s radiation-blocking properties without the weight and rigidity. Some shields are now integrated into lead aprons or vest-style protective garments, allowing for seamless neck protection. Innovations in thyroid shields continue to improve user experience and safety, addressing the need for durable, lightweight, and effective protection options. These advances are particularly beneficial for healthcare providers who wear thyroid shields for extended periods, as they reduce strain and improve comfort while maintaining high levels of radiation protection.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Promoting Thyroid Shield Use
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in ensuring thyroid shields are used correctly and consistently. Many patients may not be aware of the importance of radiation protection, especially in routine dental visits or imaging exams. Educating patients on the purpose of thyroid shields can help them understand the benefits of radiation safety and why the shield is used. In some cases, patients might have concerns about radiation exposure, and healthcare providers can address these by explaining how thyroid shields provide a barrier against harmful exposure. By promoting the use of thyroid shields and informing patients about radiation safety, healthcare professionals contribute to a culture of safety and transparency that reinforces patient trust and ensures consistent protective practices.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Thyroid Shields in Radiation Safety
Thyroid shields are a fundamental component of radiation safety protocols in medical and dental settings, offering essential protection for one of the most radiation-sensitive organs in the body. By reducing the risks associated with ionizing radiation, thyroid shields help prevent radiation-induced health issues such as thyroid cancer and other glandular disorders. From the basics of thyroid shield definition to the various types, correct usage, and maintenance, the shield’s role in medical imaging is critical. Innovations in shield materials and design have further enhanced their utility, providing lightweight, comfortable options for extended use. Consistent training, patient education, and adherence to safety protocols ensure that thyroid shields remain effective in minimizing radiation exposure. By integrating thyroid shields into regular imaging practices and adhering to safety guidelines, healthcare facilities and providers can offer safer, more reliable care that prioritizes long-term health and wellbeing. As technology advances, the importance of thyroid shields in protecting against radiation remains steadfast, underscoring their value as a crucial protective measure in modern healthcare settings.